Why in news?
- The LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory) Scientific Collaboration detected gravitational waves in 2015.
- It has recently announced that it would publish a detailed explanation of how it analyses the noise in its detectors.
What was the 2015 discovery?
- Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of space-time, arising from the merger of a pair of black holes in distant space.
- LIGO’s 2015 announcement of the discovery of gravitational waves was an exciting finding in physics for decades.
- The discovery confirmed a prediction made by Einstein.
- It stated that space-time itself can squeeze and stretch in rhythmic waves, when deformed by cataclysmic events like collision of black holes.
- The collaboration’s founders were awarded the Nobel prize in physics in 2017. Click here to know more.
What were the further observations?
- Since detecting the binary black hole (BBH) merger, the LIGO Scientific Collaboration (LSC) has made six such observations.
- Five of these were mergers of black holes in very different locations in space and with very different characteristics such as mass.
- Another was the merger of a pair of so-called neutron stars (binary neutron stars).
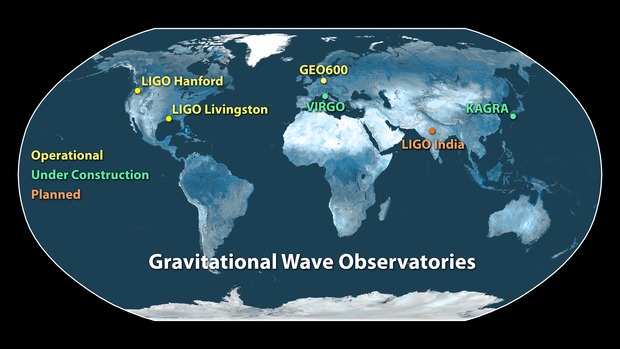
- The last few detections have been done in conjunction with another detector, Virgo (Italy-based).
What is the need for LIGO's explanation now?
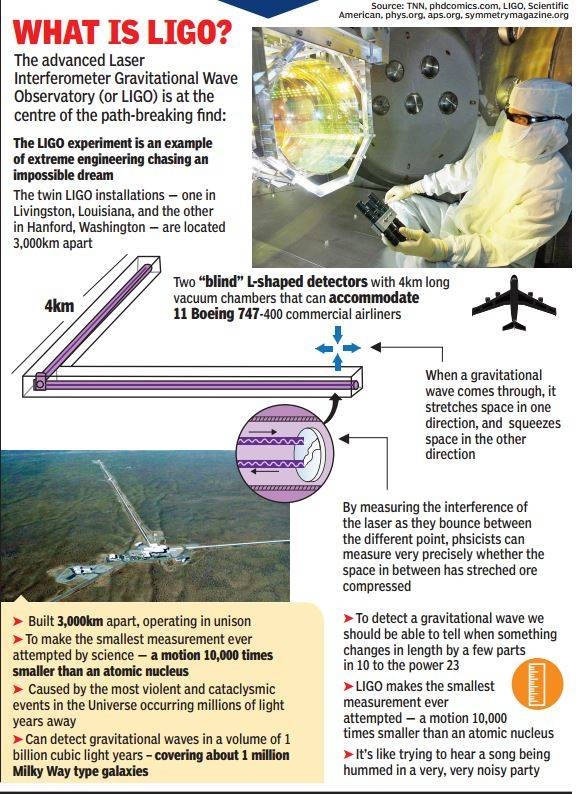
- Challenge - LIGO’s detectors aim to measure a shortening of space equivalent to about a thousandth of the width of a proton.
- This sort of measurement is swamped by natural thermal vibrations, known as noise.
- This makes picking out the signal from a gravitational wave tricky and challenging.
- The collaboration thus used sophisticated analysis techniques to remove this noise.
- Also, after the first discovery, the LSC made public its data on these techniques.
- Dispute - Analysing the data, in 2017, a group of scientists questioned the validity of the first detection.
- Weeding out noise from the signal is crucial in any such experiment.
- Some claimed that this had not been done properly by the LSC.
- They argued that the two detectors belonging to LIGO were correlated and that this led to a correlation in the noise factor.
- Other scientific investigations also uncovered a number of irregularities in the data.
- LSC - After a long silence, recently, the LSC has thus put up a clarification on its website.
- The LIGO collaboration is learnt to be in the process of preparing their paper clarifying their approach and explaining the analysis techniques.
Source: The Hindu, NewScientist

