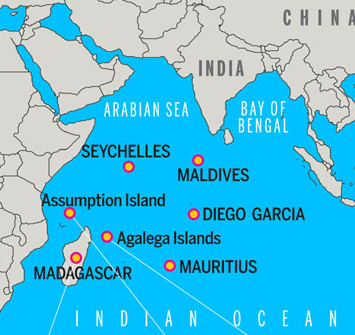
Assumption Island - Seychelles
- Assumption Island is one of the 115 islands constituting Seychelles archipelago.
- India signed a pact to develop Assumption Island, during PM Modi’s visit to Seychelles in 2015.
- Ironing out the earlier differences, India has now signed a revised agreement with Seychelles.
- Assumption Island is leased to India for the operation of a naval base and air strip by the Indian navy.
- The agreement will enable India to help Seychelles build military infrastructure for the Seychelles People’s Defence Forces.
- Seychelles has said it would “suspend” the use of military facilities on Assumption Island in case if India is at war.
- This is because it is not a military base.
- Also, other “international partners” can also use the facilities being developed by India on the island.
- It is being financed entirely by India; but Seychelles retains full ownership of the facilities and sovereign rights over the island.
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)
- The National Technical Advisory Group on Immunization (NTAGI) has recommended the introduction of HPV vaccine in the UIP.
- NTAGI is an advisory body that recommends vaccines for India’s Universal Immunization Programme (UIP).
- Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) is a group of more than 150 viruses. It is usually harmless and goes away by itself.
- However, some types cause papilloma or warts in parts of the body.
- HPV spreads by skin-to-skin contact and is the most common sexually transmitted infection.
- HPV is commonly associated with cervical cancer.
- India has one of the world’s highest burdens of HPV-related cancer and around 67,000 women die from this disease each year.
- HPV vaccines offered by private firms face clinical trial issues in India on concerns of side-effects; Supreme Court is yet to decide.
Objectionable Content
- The Ministry of Electronics and IT has highlighted that around 1300 social media URLs were blocked or removed in the last year.
- These were based on the recommendation of a government committee to deal with “objectionable content”.
- The Information Technology (IT) Act 2000 and Indian Penal Code provides for dealing with “objectionable content” posted online.
- Blocking is a sovereign power that is given to the government by virtue of Section 69A of the IT Act.
- There are concerns with the parameters on deciding a particular content as 'inappropriate' or 'objectionable'.
Pulse Polio Immunisation (PPI)
- As part of the National Immunisation Day observed on 28 January, PPI programme for 2018 was launched.
- More than 17 crore children of less than 5 years across the country will be given polio drops.
- The polio virus causes paralysis, known as an acute flaccid paralysis (AFP).
- This is characterised by sudden muscle weakness, and fever in one or more limbs.
- India reported its last polio case in 2011 and is also declared polio-free by WHO in 2014.
- However, the immunisation drive continues as polio virus is still circulating in other parts of the world.
- The injectable Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) has also been introduced recently into the Universal Immunisation Programme.
- IPV is an injectable form of polio vaccine administered alone or in combination with other vaccines including the OPV (oral polio vaccine).
Universal Immunization Programme
- Universal Immunization Programme was launched in 1985.
- The program now consists of vaccination for 12 diseases:
- tuberculosis
- diphtheria
- pertussis (whooping cough)
- tetanus
- poliomyelitis
- measles
- Hepatitis B
- diarrhoea
- Japanese Encephalitis
- Rubella
- Pneumonia( Heamophilus Influenza Type B)
- Pneumococcal diseases (Pneumococcal Pneumonia and Meningitis)
- The Indradhanush mission, launched in 2014, is to fast track the universal immunization programme.
- The mission aims at increasing the immunisation coverage to 90% by 2018.
Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- The Union Home Ministry is planning to set up the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre in Delhi.
- It would deal with cyber crimes such as financial frauds, circulation of communal and pornographic contents.
- The centre would maintain a list of suspects and the leads generated during investigations in cyber crime cases.
- This would be shared with law enforcement agencies through a "secured internal network".
- The ministry has asked states to establish a similar mechanism in every district.
- The ministry has also released a sum of Rs 83 crore in this regard.
- This would fund the setting up of a cyber forensic training laboratory-cum-training centre for police officials in each state.
Source: PIB, The Hindu
