Why in news?
A study has found that due to the seven years of higher-than-ambient temperatures, the ability of a pond to absorb carbon dioxide reduced by 50% but the release of methane nearly doubled.
What is the Greenhouse Effect?
- The GHGs are transparent to incoming solar radiation, but are opaque to some wavelengths of heat radiated from the Earth.
- So they trap heat, which leads eventually to a warming of the lower atmosphere. This is called Greenhouse effect.
- The main source of man-made carbon pollution is the burning of fossil fuels, accounting for more than 70% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- The rest comes from deforestation, the livestock industry, and agriculture.
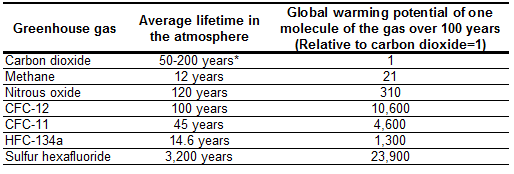
- For each greenhouse gas, a Global Warming Potential (GWP) has been calculated to reflect how long it remains in the atmosphere and how strongly it absorbs energy.
- Gases with a higher GWP absorb more energy, per pound, than gases with a lower GWP, and thus contribute more to warming Earth.
- The order of most abundant GHGs in the Earth's atmosphere is Water vapor, Carbon dioxide, Methane, Nitrous oxide, Ozone, Chlorofluorocarbons.
- Methane is about 25 times more effective in trapping the sun’s radiation in our atmosphere than carbon dioxide, which is the dominant GHG.
What is the new finding?
- The new finding is important because small ponds play an huge role in the planet’s carbon cycle, i.e., the balance between input and output of greenhouse gases.
- The ponds are also responsible for about 40% of methane emissions from inland waters.
- Findings show that warming fundamentally alters the carbon balance of small ponds over years, thereby reducing their capacity to absorb carbon dioxide and increasing emissions of methane.
- This could ultimately accelerate climate change
- This danger has been greatly overlooked.
- Until now, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) models do not take into account the amplification effects of warming on these aquatic ecosystems.
Source: The Hindu
