What is the issue?
Manipur suffered a setback to its finances when the state lost the special status owing to the Fourteenth Finance Commission recommendations.
What is Special Category Status?
- The Constitution does not include any provision for categorisation of any State in India as a Special Category Status (SCS) State.
- But, recognising that some regions in the country were historically disadvantaged in contrast to others, the SCS was introduced by Fifth Finance Commission in 1969. It provides for additional Central assistance and tax concessions.
- The NDC granted this status based on a number of features including hilly and difficult terrain, presence of sizeable tribal population, strategic location along international borders, economic and infrastructural backwardness etc.,
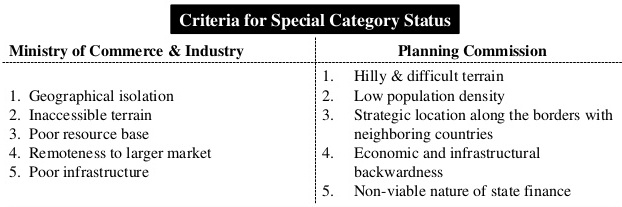
What kind of assistance do SCS States receive?
- Following the constitution of the NITI Aayog and the recommendations of the 14th Finance Commission (FFC), Central plan assistance to SCS States has been subsumed in an increased devolution of the divisible pool to all States (from 32% in the 13th FC recommendations to 42%).
- They enjoy concessions in excise and customs duties and income tax rates.
- Besides, assistance to Centrally Sponsored Schemes for SCS States was given with 90% Central share and 10% State share.
Why A.P. claimed for SCS status recently?
- Following the bifurcation of A.P., Andhra lost a large volume of its revenue due to Hyderabad remaining the capital of Telangana.
- In a debate in the Rajya Sabha on the A.P. Reorganisation Act on February 20, 2014, then Prime Minister of India had said that SCS would be extended to the successor State of Andhra Pradesh for a period of five years.
- This oral submission by the then PM has been the basis for A.P.’s claim to the status.
What has been the Centre’s response to A.P.?
- A.P. does not qualify as a Special Category State. It has neither geographical disadvantages nor historical disadvantages such as socio-economic and infrastructural backwardness.
- Hence offering it the SCS would give impetus to every other state to demand for the same.
- Instead, Centre announced a package to grant special assistance to Andhra Pradesh, wherein an amount equivalent to what the state might have got as a special category state will be compensated by Centre through externally aided projects for five years.
- The special package offered meets most of the reasonable expectations of a State struggling to recover from bifurcation and dealing with the imminent loss of the capital city and its revenues.
- It included Polavaram irrigation project declared a national project i.e Centre would meet the financial needs.
- Also, Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) would issue two specific notifications on tax concessions being extended to A.P.
What does it mean for Manipur?
- Loss of special category status would mean that Manipur would no more get the 90% Central grants assistance and remaining 10% as loan, which it used to enjoy for taking up developmental projects and schemes in the State.
- Manipur would now get only 30% Central grant and the remaining has to be either arranged by itself or taken as loan from the Centre.
- While presenting the Budget for 2016-17 last year, the Chief Minister of Manipur acknowledged the hit on state’s finances due to restructuring of central assistance to the state.
- Even though higher devolution of taxes was positive for the state’s finances, it was not enough to meet the state’s Plan revenue expenditure.
Source: Indian Express & The Hindu
