SEBI’s Measure to Increase Market Liquidity
- In April, SEBI had relaxed certain regulatory requirements related to rights issues and initial public offerings (IPOs) to help companies to raise funds during this pandemic.
- It allowed any listed entity with a market capitalization of at least Rs.100 crore could use the fast- track route for a rights issue.
- Earlier, the norm was ₹250 crore for such offerings.
- Further, any company that had been listed for 18 months was permitted to raise funds through a fast- track rights issue. Earlier it was 3 years.
- Also, the minimum subscription requirement to make an issue successful was lowered from the earlier 90% of the offer size to 75%.
- Recently, SEBI has allowed companies to make 2 qualified institutional placements (QIPs) with a gap of just 2 weeks between them.
- This is a significant move as the earlier regulations mandated a minimum gap of 6 months between two such issuances.
- It also permitted promoters to increase their stakes in their companies through preferential allotments by up to 10% without triggering an open offer, the cap was earlier set at 5%.
- SEBI allowed the above relaxation only for the current financial year.
- These moves would help in enhancing liquidity in the market as companies would be able to better time fund-raising while promoters could also acquire shares at a time when valuations were quite low compared with the historic highs.
SEBI
- It was first established in 1988 (originally formed in 1992) as a non-statutory body for regulating the securities market.
- It was given Statutory Powers through the SEBI Act, 1992.
- It was constituted as the regulator of capital markets in India under a resolution of the Government of India.
- After the amendment of 1999, collective investment schemes were brought under SEBI except Nidhis, chit funds and cooperatives.
- The SEBI is managed by its members, which consists of the following:
- The chairman is nominated by the Union Government of India.
- Two members, i.e., Officers from the Union Finance Ministry.
- One member from the Reserve Bank of India.
- The remaining five members are nominated by the Union Government of India, out of them at least three shall be whole-time members.
RBI Norms for NBFC’s
- A housing finance company is considered a non-banking financial company (NBFC) under the RBI’s regulations.
- A company is treated as an NBFC if its financial assets are more than 50% of its total assets and income from financial assets is more than 50% of the gross income.
- RBI has proposed stringent norms for housing finance companies by mandating 75% of their home loans to individual borrowers by 2024.
- Recently, RBI has proposed the definition of qualifying assets for housing finance companies (HFCs).
- It defined ‘qualifying assets’ as loans to individuals or a group of individuals, including co-operative societies, for construction/purchase of new dwelling units, loans to individuals for renovation of existing dwelling units, lending to builders for construction of residential dwelling units.
- Non-Housing loans - All other loans, including those given for furnishing dwelling units, loans given against mortgage of property for any purpose other than buying/construction of a new dwelling units or renovation of the existing dwelling units.
- Under new definition at least 50% of net assets should be in the nature of ‘qualifying assets’ for HFCs, of which at least 75% should be towards individual housing loans.
- Such HFCs which do not fulfil the criteria will be treated as NBFC – Investment and Credit Companies (NBFC-ICCs).
- They will be required to approach the RBI for conversion of their Certificate of Registration from HFC to NBFC-ICC.
- The NBFC-ICCs which want to continue as HFCs would have to follow a roadmap to make 75% of their assets individual housing loans.
- The central bank also proposed a minimum net-owned fund (NOF) of ₹20 crore as compared to ₹10 crore now.
- Existing HFCs would have to reach ₹15 crore within a year and ₹20 crore within two years.
Role of Anti-cyclone in North-east Asia
- New research has revealed a link between an increase in extreme summer heat events in Northeast Asia and the role of anticyclones in the region.
- Extreme heat events have increased across the world and are responsible for a large number of deaths and harming crops and livestock as well.
- Nearly half of the magnitude of the 2018 extreme heat event across China and Japan was caused by anomalous anticyclones in Northeast Asia.
- There are mainly 2 factors which make the extreme heat events more likely to occur over Northeast Asia.
- Dynamic (anticyclone) and thermodynamic (mean temperature shifts to warmer states and increasing greenhouse gases) changes in the atmosphere.
- Anticyclones similar to those in 2018 became more common and worse in recent decades (1991-2017) than the past (1958-1990).
- The more extreme the heat event, the larger the contribution of the thermodynamic change will be.
Anti-Cyclone
- An anticyclone is a large-scale circulation of winds around high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere, counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
- It cause clear skies and high temperatures and responsible for settled weather conditions.
- Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure.
- It can form within warm core lows such as tropical cyclones, due to descending cool air from the backside of upper troughs such as polar highs, or from large scale sinking such as the subtropical ridge.
- The evolution of an anticyclone depends upon variables such as its size, intensity, and extent of moist convection, as well as the Coriolis force.
Artic Sea
- It is located mostly in the Arctic North Polar Region in the middle of the Northern Hemisphere, besides its surrounding waters the Arctic Ocean is surrounded by Eurasia and North America.
- It is partly covered by sea ice throughout the year and almost completely in winter.
- The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans and it is also known as the coldest of all the oceans.
- The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Sea.
- It is sometimes classified as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean, and it is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.
- The Arctic Ocean's surface temperature and salinity vary seasonally as the ice cover melts and freezes.
- Its salinity is the lowest on average of the five major oceans, due to low evaporation, heavy fresh water inflow from rivers and streams, and limited connection and outflow to surrounding oceanic waters with higher salinities.
Decline in Artic Sea Ice
- Sea ice arises as seawater freezes, because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface.
- Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oceans.
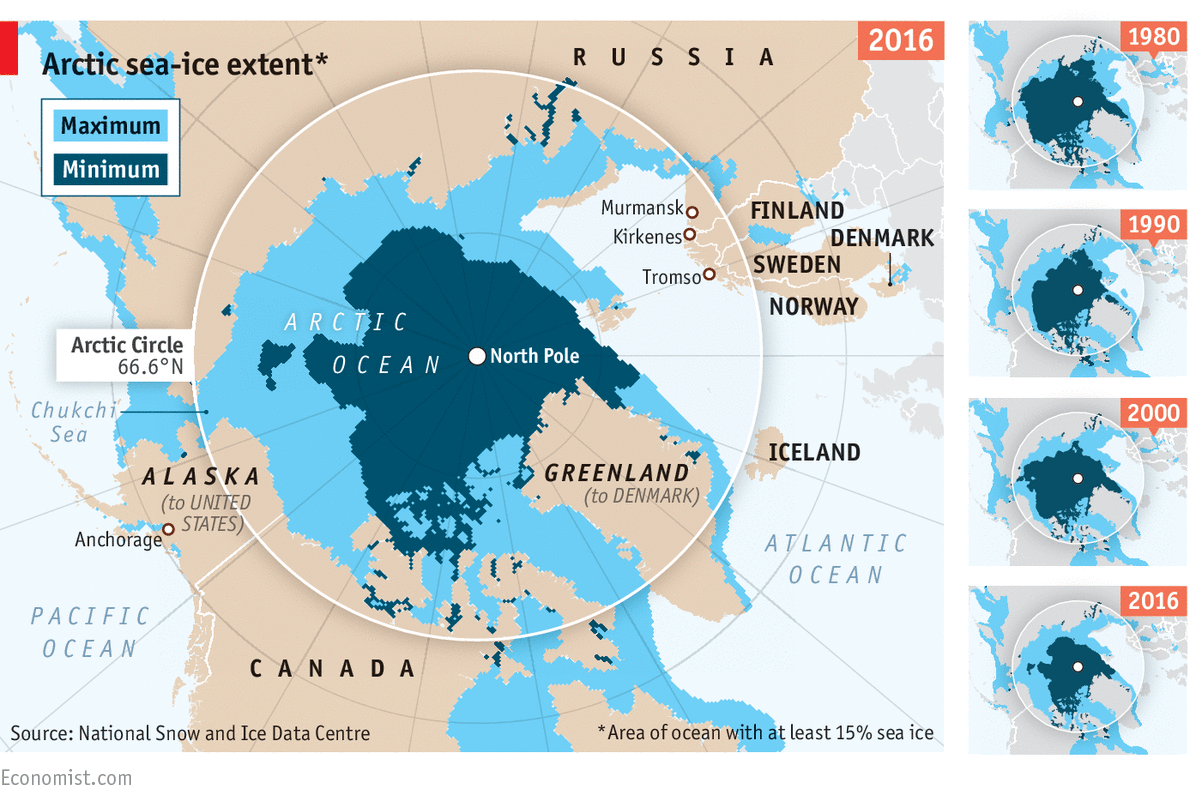
- Recently, National Centre of Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR) has observed the largest decline in the Arctic Sea ice in the last 41 years.
- According to recent observations in the last 40 years (1979-2018), the sea ice has been declining at 4.7% per decade, while the current declining rate was found to be 13% in July 2019.
- Thus, it has been noted that the volume of ice formation during winters is unable to keep pace with the volume of ice loss during summers.
- Additionally, it has been predicted that if this trend continues, there would be no ice left in the Arctic Sea by 2050.
- The decrease of the Arctic Sea ice area and the increase in the duration of summer and autumn seasons affected the local weather and climate over the Arctic Ocean and its marginal seas.
- It may affect other components of the climate system such as reduction of heat, water vapor, and other material exchange between the atmosphere and the sea.
- The northern hemisphere experienced record high-temperature rise, especially during the spring and summer months.
National Centre of Polar and Ocean Research
- It was established as an autonomous Research and Development Institution of the Ministry of Earth Sciences in 1998.
- It is located in Goa.
- Earlier known as National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research (NCAOR), NCPOR is India’s premier R&D institution responsible for the country’s research activities in the Polar and Southern Ocean realms.
- It is the nodal agency for planning, promotion, coordination and execution of the entire gamut of polar and southern ocean scientific research in the country as well as for the associated logistics activities.
World Crocodile Day
- World Crocodile Day is celebrated on 17th June.
- The day is a global awareness campaign to highlight the plight of endangered crocodiles and alligators around the world.
- Crocodile spices found in India includes
- Mugger or Marsh Crocodile
- Estuarine or Saltwater Crocodile
- Gharial or River water Crocodile
- Human-crocodile conflict Hotspots in India includes
- Vadodara in Gujarat (in Vishwamitri river)
- Kota in Rajasthan,
- Bhitarkanika in Odisha
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands (Culling had been recommended a few years back in the Andaman and Nicobar islands by the forest department to the MoEFCC)
Indian Crocodile Conservation Project
- The Crocodile Conservation Project was launched in 1975 in different States.
- The Gharial and Saltwater crocodile conservation programme was first implemented in Odisha in early 1975 and subsequently the Mugger conservation programme was initiated.
- Gharial crocodile project started in Tikarpada (1975) aims to increase the sighting to five crocodiles per kilometer length of water.
- As a result of the programme, the estimated number of the saltwater crocodiles increased from 96 in 1976 to 1,640 in 2012 in India.
CrocBITE
- CrocBITE is an online database of crocodile attacks reported on humans.
- The non-profit online research tool helps to scientifically analyze crocodile behavior via complex models.
- Users are encouraged to feed information in a crowdsourcing manner, the uploaded information needs to be verifiable.
- The database provides key insights into crocodile attack patterns and draws inferences to save human lives.
- The information is vital for Australia and Africa where such attacks are more likely than in other parts of the world.
- This is the only database of its kind with such comprehensive collection of information made available online.
Source: DTE, the Hindu
