Mains: GS-III – Economy
India has reshaped its economy by making digital transformation a key driver of growth; introduced wide-ranging reforms to improve Ease of Doing Business (EoDB).
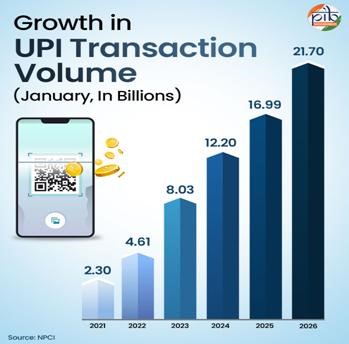
Mains: GS III – Economy
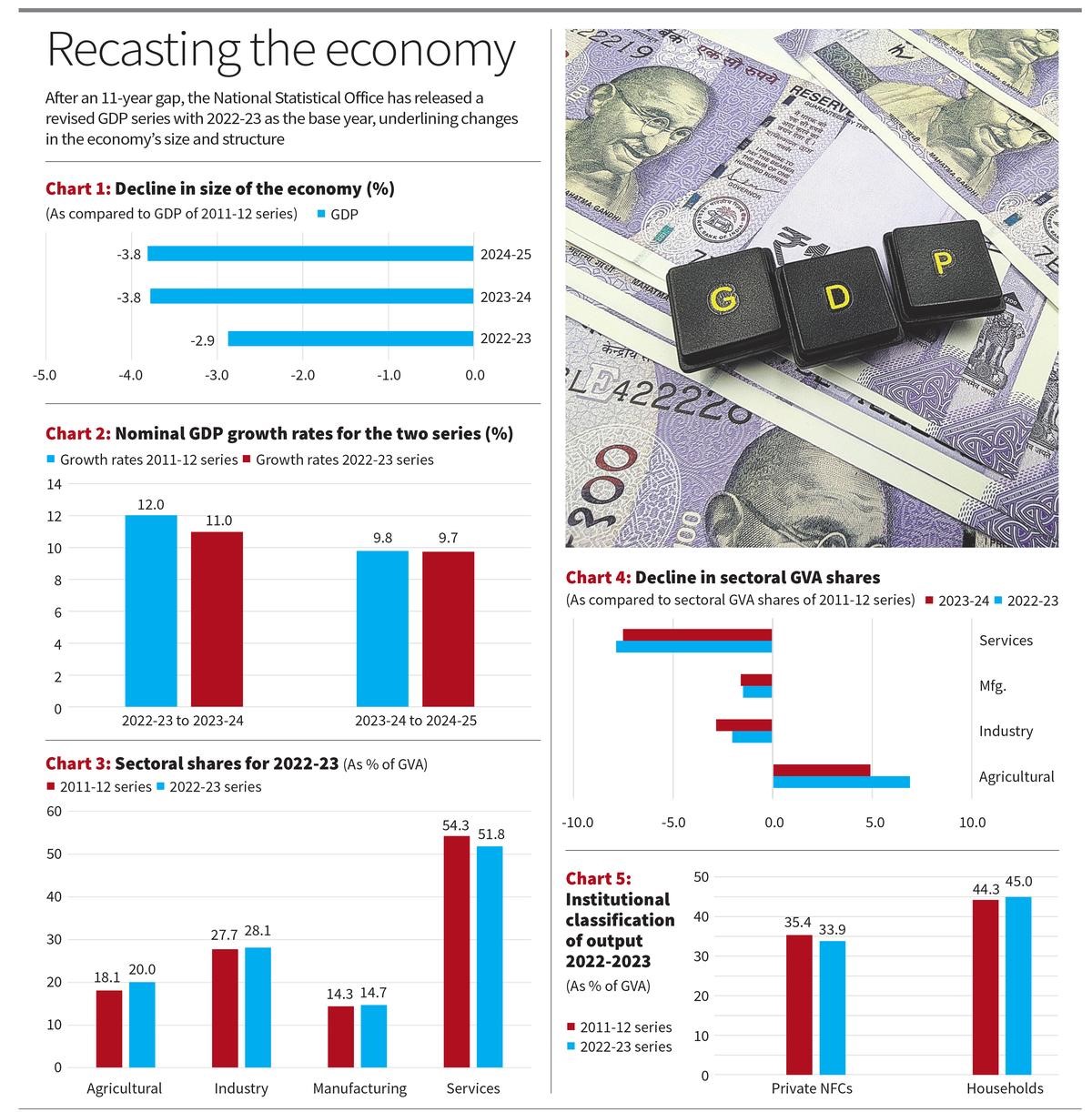
Recently the GDP revision introduced 2022-23 as the base year replacing 2011-12 series.
Preparing for the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) examination is an exceptionally demanding process, requiring not only a solid grasp of core subjects but also a thorough and up-to-date understanding of current affairs. Given the vastness of the UPSC syllabus, current events play a critical role in shaping the examination questions. Success in the UPSC requires aspirants to stay continuously informed about the latest national and international developments.
The IAS Parliament platform is a highly reliable and comprehensive resource specifically designed to meet this need. It provides crucial news and insights across a spectrum of relevant topics, including:
The platform also covers vital sectors such as agriculture, education, and health. By providing regular updates on governmental functions and departmental activities, IAS Parliament serves as an ideal and centralized source for current affairs preparation.
To ensure aspirants are comprehensively prepared, IAS Parliament offers a structured and rich daily content schedule:
Beyond informative articles, the IAS Parliament integrates essential tools for self-assessment and progress tracking:
To maintaining a rigorous focus on current affairs is fundamental to UPSC preparation. The IAS Parliament stands out as a one-stop-shop that provides reliable, comprehensive, and regularly updated coverage of current affairs. Its user-friendly interface and diverse range of resources—from daily digests and focused articles to quizzes and analytical content—make it an indispensable tool for every serious UPSC aspirant aiming for success.
Also Read: