7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
What is the issue?
The transition to fifth-generation cellular networks (known as 5G for short) is soon to happen.
What is the change in the making?
What exactly is 5G?
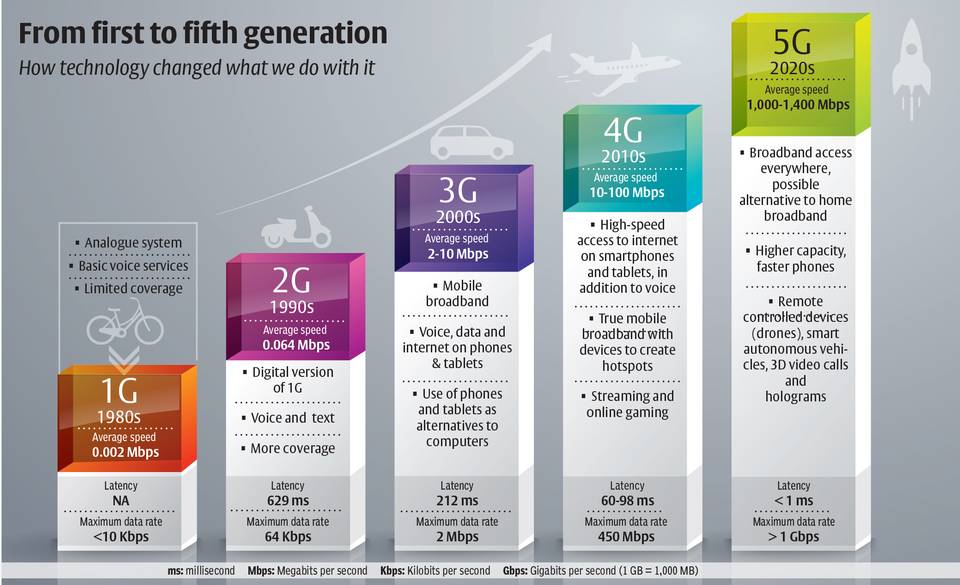
What are the key benefits?
Source: Business Line