7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
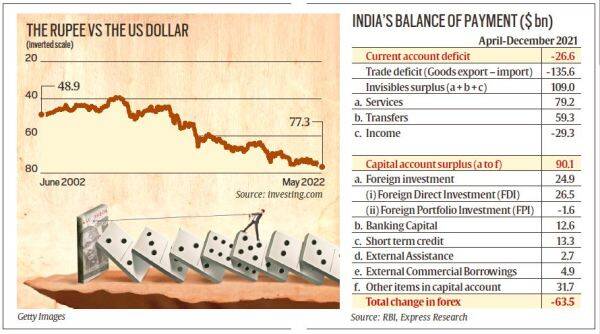
Recently, the Indian rupee hit an all-time low exchange rate of 77.6 against the US dollar.
Currency depreciation is a fall in the value of a currency in terms of its exchange rate versus other currencies. It can occur due to factors such as economic fundamentals, interest rate differentials, political instability, or risk aversion among investors.
The sum of all transactions recorded in the balance of payments should be zero; however, exchange rate fluctuations and differences in accounting practices may hinder this in practice.
Negative impacts
Positive impacts
References