The extent of vegetation in the Antarctic Peninsula has increased 14 times in just 35 years.
One can suffer serious sunburn whilst there as the snow acts as a reflector which reflects nearly all the ultraviolet rays.
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants and Lichen is a hybrid colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among filaments of multiple fungi species.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has estimated that the Earth as a whole is warming at the rate of 0.14-0.18 degrees Celsius per decade.
In March 2022, Antarctica experienced its most intense heatwave — temperatures in East Antarctica soared to 39 degrees Celsius above normal.
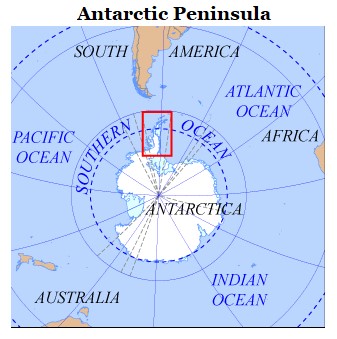
Antarctic Peninsula is the long, mountainous extension of Antarctica that points north towards South America.
Antarctica has already lost 280% more ice mass in the 2000s and 2010s than it lost in the 1980s and 1990s.
Adrian Campbell 3 months
This Chill Guy Clicker customisation adds a whimsical element to the game, allowing players to showcase their originality and individuality.