7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
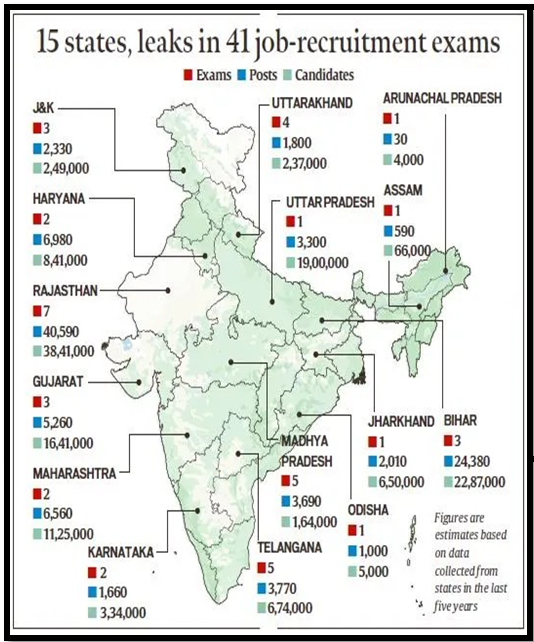
Recently, the Bihar Assembly has passed Bihar Public Examinations (PE) (Prevention of Unfair Means) Bill, 2024.
|
Attributes of a Good Exam |
|
|
The Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act |
|
In 2023, States like Rajasthan, Jharkhand, Uttarakhand, and Gujarat have passed an anti-cheating legislations.