7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Recently, Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita Bill 2023 was introduced in the Lok Sabha to replace Indian Penal Code (IPC), 1860.
Lord Thomas Babington Macaulay is said to be the chief architect of codifications of criminal laws in India.
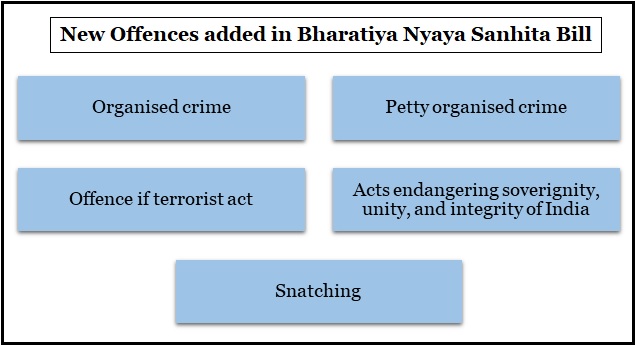
The new Bill on IPC completely repeals the offence of sedition which is reflected in Section 124A of the IPC. The bill aims to give justice not punishment.
|
Committees for reform of Criminal Laws |
|
References