Biodiversity is declining more quickly inside key protected areas than outside them, according to a new study by the Natural History Museum (NHM), London.
Critical Biodiversity Areas (CBAs) are Ecosystems and areas such as wetlands that are crucial for biodiversity and 22% of which is protected.
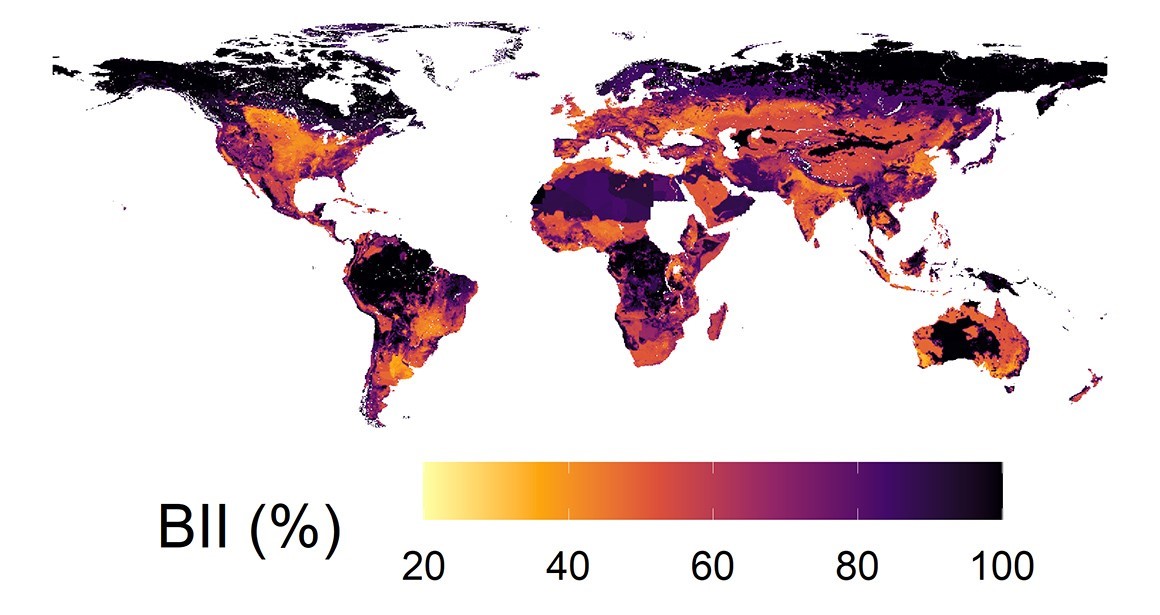
53 % of land in India is under conversion for urban, industrial, and agricultural purposes.

Prohibition of mining activities in National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries (“Protected Areas”) shall also extend to an Eco sensitive area up to one kilometre (“km”) from the boundary of the Protected Area.
Quick Facts
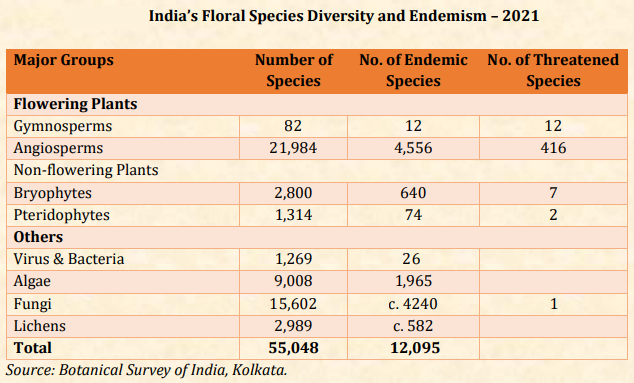
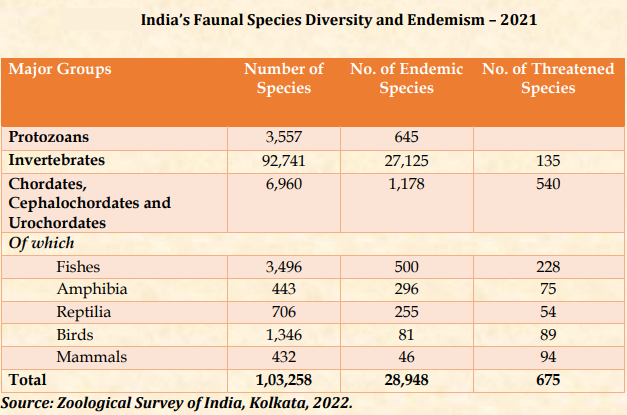
Indian Express | Biodiversity Intactness Index
Wilma Eilerman 4 months
This paper offers a compelling overview of biodiversity decline within protected areas, highlighting critical gaps in current strategies. Thank you for shedding light on this urgent issue! The analysis of contributing factors is particularly insightful and well-researched. Further research could explore community-based conservation or ecosystem restoration as potential solutions. Papa's Freezeria Investigating policy incentives for sustainable land management outside park boundaries might also prove fruitful.