7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Why in News?
Regional Rural Banks losing ground to private banks amid tech challenges.
|
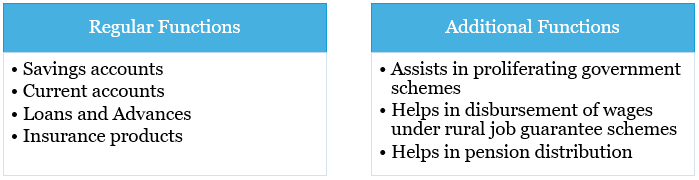
Status of RRB’s in India |
|
|
Digital deficit |
|
|
Digital deficit in RRBs |
|
Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) are the assets which ceases to generate income for the bank.
What are the steps taken to improve the status of RRB’s?
A 2022 National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) report highlighted that RRBs need to enhance their loan recovery processes through technology, policy improvements, and best Practices.