Over the past few years, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has radically altered the nation’s exchange rate policy, shifting from a relatively flexible regime to an inflexible one.
Depreciation is the increase in exchange rate meaning that the price of foreign currency (dollar) in terms of domestic currency (rupees) has increased.
Appreciation is the price of domestic currency (rupees) in terms of foreign currency (dollars) increases.
Devaluation in a fixed exchange rate system is the increase in exchange rate to make the domestic currency cheaper and Revaluation is the decrease in exchange rate to make domestic currency costlier.
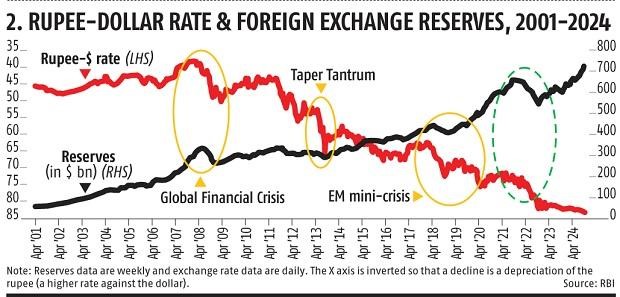
From February to October 2022, RBI sold $105 billion in reserves to prevent depreciation after the US Federal Reserve started to raise interest rates aggressively to fight inflation.
The real exchange rate (RER) between two currencies is the product of the nominal exchange rate (the dollar cost of a euro, for example) and the ratio of prices between the two countries.
During the boom from 2002 to 2011, the rate appreciated by 16 % thereby dampening the excess demand and inflation that emerged during this period.
From June 2002 to September 2018, reserves swelled from $59 billion to over $400 billion as the RBI absorbed large capital inflows.
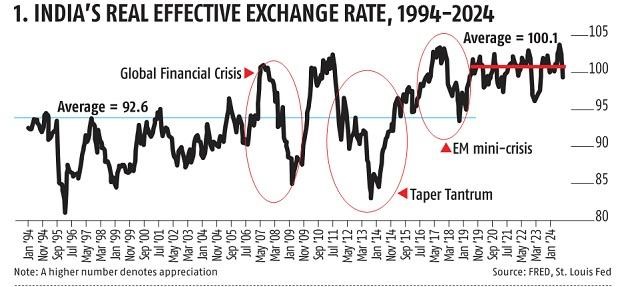
The taper tantrum refers to a period of market volatility in 2013 triggered by the US Federal Reserve's announcement to gradually reduce its bond-buying program.