Why in news?
Chhattisgarh has intensified its crackdown on Maoist insurgents since December 2023, resulting in many arrests and surrenders.
What is Maoism?
- It is a form of communism developed by Mao Tse Tung.
- It is a doctrine to capture State power through armed insurgency, mass mobilization, and strategic alliances.
- The Maoists also use propaganda and disinformation against State institutions.
- Mao called this process the 'Protracted People's War,' focusing on the 'military line' to capture power.
- Prioritizes rural agrarian communities as the primary revolutionary force.
What are the Most Affected Regions?
- Ministry of Home Affairs identifies the following states as affected by Left Wing Extremism, though to varying degrees:
- Chhattisgarh
- Jharkhand
- Odisha
- West Bengal
- Andhra Pradesh
- Telangana
- Maharashtra
- Madhya Pradesh
- Kerala
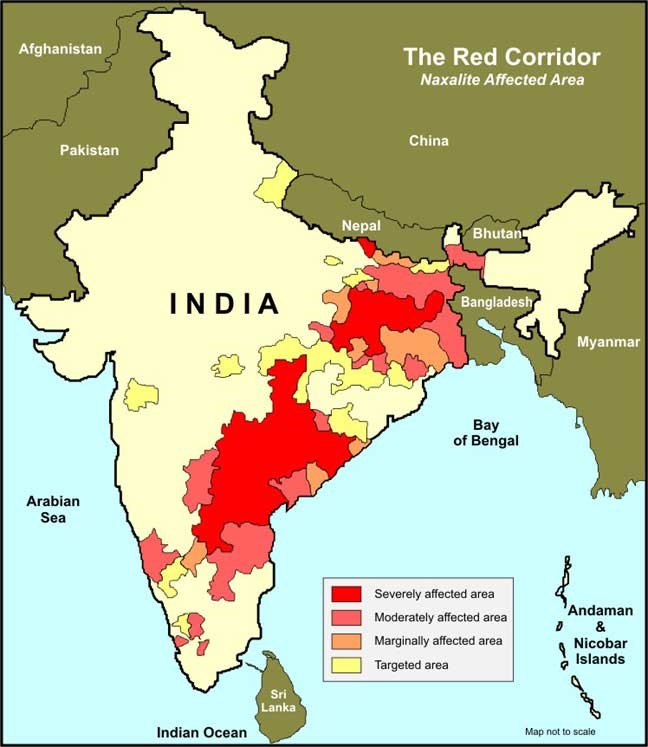
- Decline of Maoist Influence - in Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Jharkhand, and Bihar, where they once had influence.
- Reduction in Affected Areas - have decreased from 220 (early 2000s) to less than 40 (as per Ministry of Home Affairs reports).
- Violence is now concentrated in a few pockets of Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra.
What are the Challenges in Dealing with Maoism?
- Security Challenges - Entrenched Insurgency - Maoists control remote tribal regions, creating a security vacuum and running parallel governance systems.
- Violence & Intimidation - Maoist cadres use terror tactics to suppress local resistance and hinder governance.
- Socio-Economic Challenges - Underdevelopment - Lack of roads, healthcare, and education fuels discontent, which Maoists exploit.
- Tribal Displacement- Infrastructure projects cause displacement, providing Maoists with easy recruits.
- Administrative Challenges - Governance Vacuum - Weak state presence allows Maoists to dominate and control local administration.
- Coordination Issues - Differences between central and state agencies hinder counter-insurgency efforts.
- Ideological & Perception Challenges - Public Sympathy - Some intellectuals and activists support Maoist ideology, complicating efforts to counter extremism.
- Human Rights Concerns - Aggressive security actions risk civilian casualties, fueling further alienation.
What are Legal Framework to Deal with Maoism?
Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA), 1967
- Objective- Prevent unlawful activities that threaten India's sovereignty.
- Key Provisions - Unlawful Associations- Govt. can ban organizations disrupting national integrity.
- Terrorist Organizations- CPI (Maoist) designated as a terrorist outfit (2009).
- Strict Penalties- Criminalizes membership, support, and fundraising for such groups.
- Extended Detention- Allows detention without charge for up to 180 days.
Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA), 1958
- Objectives- Empower armed forces to maintain public order in disturbed areas.
- Key Provisions - Disturbed Areas- Govt. can declare regions as disturbed under AFSPA.
- Special Powers- Armed forces can use force, arrest without a warrant, and conduct searches.
- Legal Immunity- Protection from prosecution without central govt. approval.
National Investigation Agency (NIA) Act, 2008
- Objective- Establish NIA as India's central counter-terrorism agency.
- Key Provisions - NIA Formation- Investigates offenses related to national security.
- Scheduled Offenses- Covers laws like UAPA, Atomic Energy Act, etc.
- Concurrent Jurisdiction- NIA can take over state police cases with central approval.
Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act (PESA), 1996
- Objective - Strengthen self-governance in tribal regions.
- Key Provisions - Empowers Gram Sabhas - Control over natural resources and local disputes.
- Consultation on Land Issues - Required before land acquisition in Scheduled Areas.
- Local Governance -Enhances tribal autonomy over development programs.
What are Steps Taken by the Indian Government to Counter Maoism?
Security Measures
- Operation SAMADHAN - A focused counter-insurgency strategy integrating intelligence, modern technology, and security forces.
- Deployment of CAPFs -Increased presence of CRPF, BSF, ITBP, and state police in affected areas.
- Special Forces - Formation of elite anti-Maoist units like Greyhounds (Telangana), CoBRA (CRPF), and STF (various states).
- Unified Command - Coordination between state and central forces for joint operations.
Development Initiatives
- Road Connectivity Project for LWE Areas- Focuses on constructing roads in Maoist-affected districts.
- Skill Development Schemes - Programs like ROSHNI and Skill Development Scheme in 47 LWE districts to provide employment.
- Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) - Set up for tribal children to improve education access.
- Special Central Assistance (SCA) - Additional funding for LWE-affected districts for infrastructure and welfare projects.
What are the Rehabilitation and Surrender Policies?
- Surrender and Rehabilitation Scheme - Financial assistance, vocational training, and housing support for surrendered Maoists.
- Relief for Affected Families - Compensation for civilians and security personnel affected by Maoist violence.
What Lies ahead?
- Dealing with Naxalism in India needs a balanced strategy. Focus on both security measures and root causes like poverty.
- Improve infrastructure, education, and job opportunities in affected areas. Engage in open dialogue with local populations to strengthen ties.
- Combining security efforts with socio-economic development and community engagement can help India effectively address Naxalism and create a safer future.
To Solve Mains question – Click Here
Refer to - Indian Express| MAOIST
