7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Why in news?
In a recently released white paper, China announced that it would develop a Polar Silk Road (PSR).
What is the development in the Arctic region?
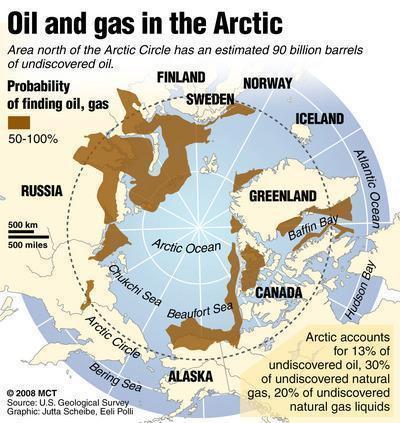
What is China looking for?
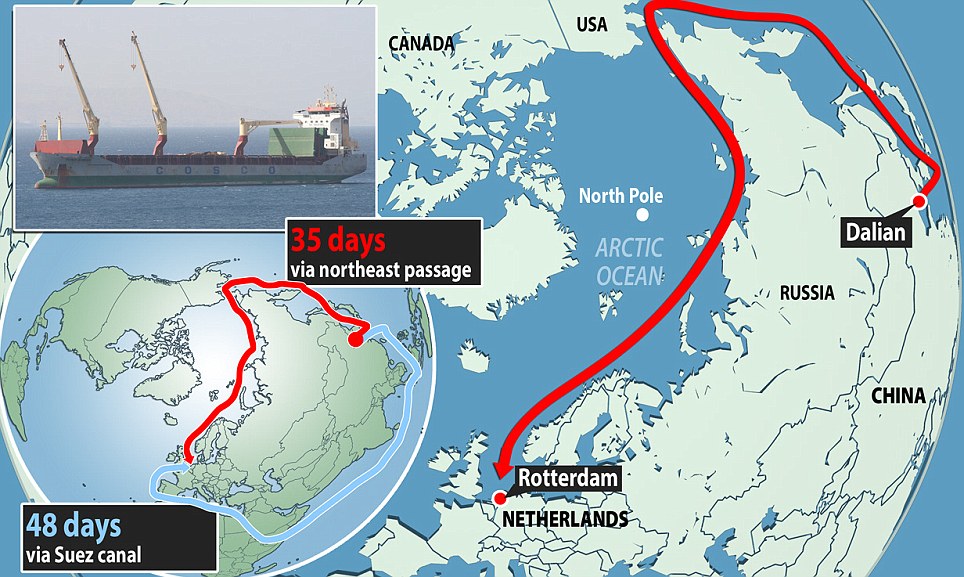
What is Russia’s role in this regard?
Source: The Hindu