7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Nearly three years into the pandemic, China is sticking with a strict COVID-19 containment policy that has caused mounting economic damage and widespread frustration.
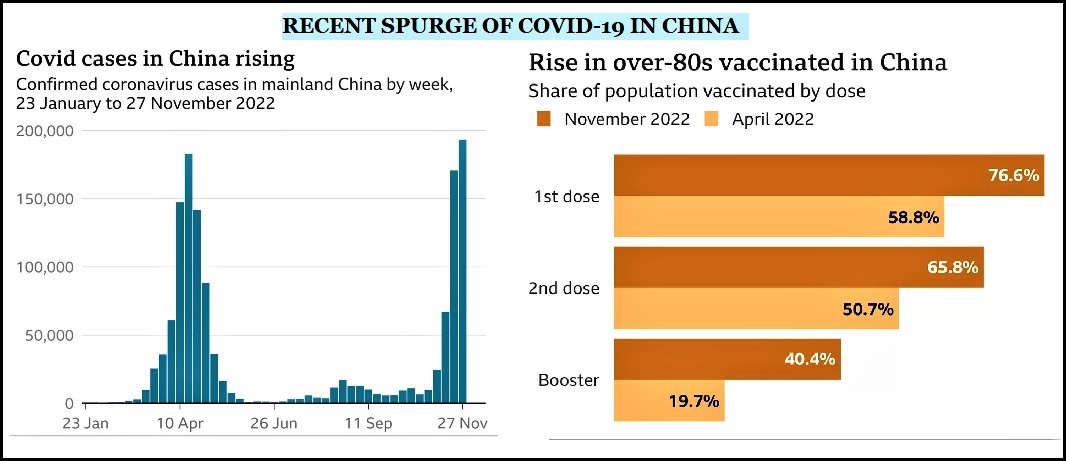 What effect have zero covid policies had on China's economy?
What effect have zero covid policies had on China's economy?
References