7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Why in News?
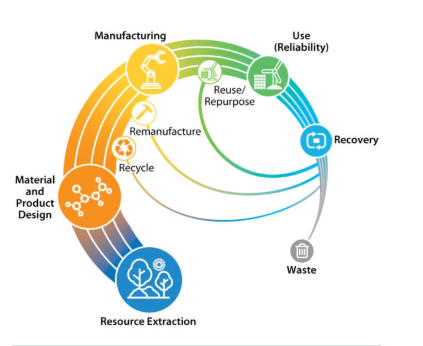
Recently, G20 Indian Sherpa India's Amitabh Kant said that circular economy could generate a market value of over $2 trillion and create 10 million jobs by 2050.
Reference