The Union Cabinet recently has approved the Clean Plant Programme (CPP) under Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture.
Horticulture consist of fruits, vegetables, and flowers, spices mushroom, medicinal and aromatic plants. India is the 2nd largest producer of fruits and vegetables in the world after China.
|
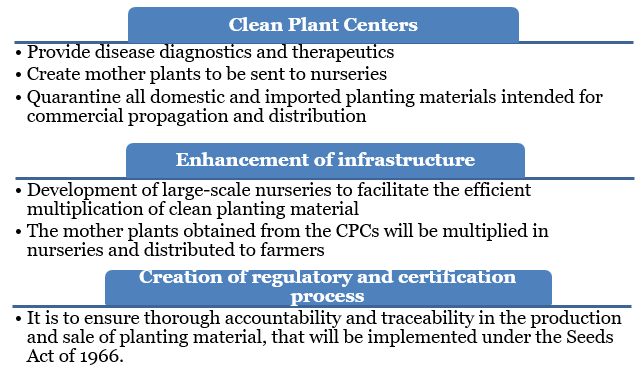
Clean Plant Centers |
||
|
||
|
CPC Location |
Crop |
Linked ICAR Institute |
|
Pune, Maharastra |
Grapes |
National Research Center for Grapes, Pune, |
|
Bikaner, Rajasthan |
Citrus fruits |
Central Institute of Arid Horticulture, Bikaner. |
|
Nagpur , Maharastra |
Citrus fruits |
Central Citrus Research Institute, Nagpur. |
|
Solapur, Maharastra |
Pomegranate |
National Research Center on Pomegranate – Solapur. |
|
Bengaluru, Karnataka |
Mango, Guava, Dragon Fruit and Avocado |
Indian Institute of Horticultural Research, Bengaluru. |
|
Srinagar , Jammu and Kashmir |
Temperate Fruits - Apple, Almond, Walnuts, etc. |
Central Institute of Temperate Horticulture (CITH), Srinagar |
|
Mukteshwar, Uttarkhand |
Temperate Fruits - Apple, Almond, Walnuts, etc. |
Regional Station of CITH, Mukteshwar. |
|
East India |
Tropical and Subtropical Plants |
East India Horticulture center in West Bengal and Jharkhand. |
|
Lucknow |
Mango, Guava, Litchi |
Central Institute for Subtropical Horticulture , Lucknow. |
|
Benefits of CPP |
|
|
Farmers |
|
|
Nurseries |
|
|
Consumers |
|
|
Exports |
|
|
Inclusion |
|
|
Alignment with Broader Initiatives |
|
|
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) |
|