7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Himachal Pradesh witnessed a heavy rainfall along with landslides in which at least 22 people died.
According to the Indian Meteorological Department, an event of extremely heavy rainfall is determined as a cloudburst when "10 cm rainfall is received at a station in one hour”
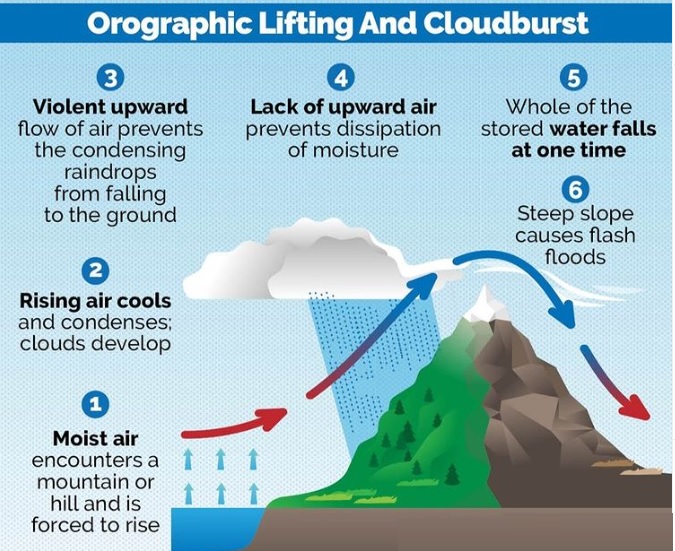
Recent cloudbursts
References