What is the issue?
Given the significance of MSMEs (micro, small and medium-sized enterprises), enhancing the credit availability to the sector is essential.
What is MSMEs’ composition in India?
- India’s MSME sector - 63-million-enterprises
- 3.3 lakh MSMEs - Between Rs 5 crore and Rs 70 crore annual turnover.
- Manufacturing, services and trade each comprise about 1/3rd of the overall MSME sector.
What are the key contributions of the MSME sector?
- About 45% to the overall manufacturing output
- More than 40% of the country’s exports
- Over 28% of GDP
- Employment for about 111 million people (Stands next only to the agricultural sector)
Concerns
- A majority of the MSMEs do not have websites.
What are the recent government initiatives?
- Change in the MSMEs definition to allow for turnover-based thresholds with enhanced limits. (Earlier–only based on investments)
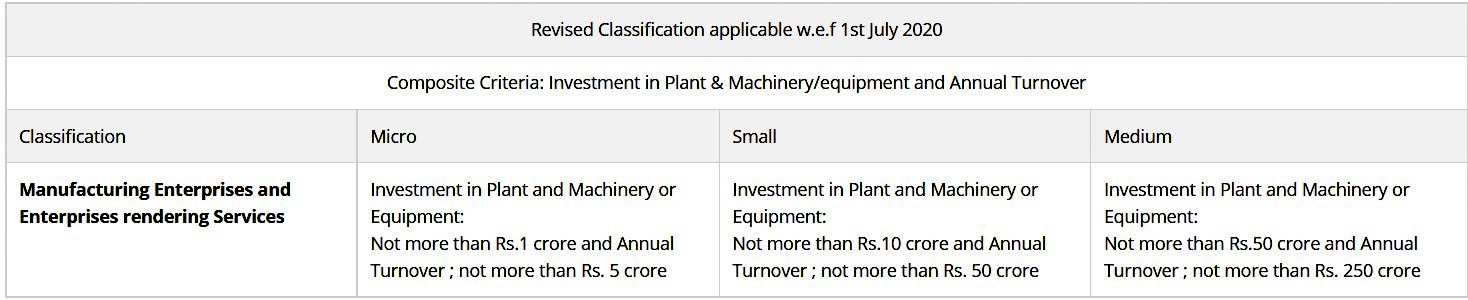
- Services were included alongside manufacturing under the MSME category.
- Wholesale and retail trade were classified as MSMEs by the RBI for the purposes of accessing credit.
- To address the effects of Covid-19 on MSMEs, the government announced a series of stimulus measures:
- Rs 6.28 lakh crore package
- an equity infusion of Rs 88,000 crore into the ECGC (Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India)
- loan guarantees of Rs 1.1 lakh crore
- Factoring Regulation Bill in 2020 to improve the availability of credit to MSMEs
- an emergency credit line guarantee scheme (ECLGS) of Rs 1.5 lakh crore
Did credits reach the enterprises?
- Banks, in the absence of appropriate incentives, disbursed funds only to borrowers with good record of paying back.
- Banks’ hesitation to lend leaves MSMEs struggling to find funds to manage their businesses.
- 84% of MSME debt, amounting to about Rs 58.4 lakh crore, is sourced from informal sources.
How can credits be better offered to MSMEs?
Efficient use of India’s digital platform stacks, protocols and frameworks -Aadhaar, UPI, eKYC, eSign, GSTN, IT, Account Aggregator, etc.
- Ascertaining borrower’s financial health from the GSTN, bank and IT data
- Processing eKYC through Aadhaar
- e-Signing of documents
- Transferring money via UPI into bank accounts that are mostly Aadhaar-linked too.
- Sharing of financial information with consent of the borrower, enabled through digital platforms.
- Open Credit Enablement Network (OCEN) - A related initiative that can democratise lending by making lenders of service providers, with access to potential borrowers.
- E.g., a food delivery company can offer loans to restaurants using the order history of the restaurant, its GST, bank balance and IT, etc.
What is needed for effective implementation?
- Coordination among multiple entities - regulators, ministries, lenders, MSMEs and third-party providers
- Enhancing digital awareness
- Framing of a techno-legal policy that empowers MSMEs
Source: Financial Express
