7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
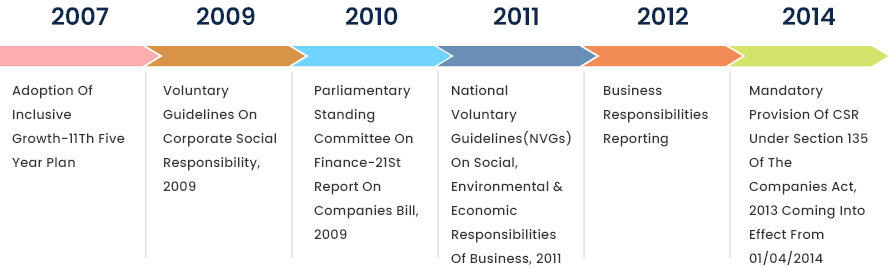
A decade ago, India became the first country to legally mandate Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR).

India was the first country to have statutorily mandated CSR for specified companies.
|
List of proposed CSR activities |
|
|
Activities Not Falling in the Ambit of CSR |
|
What are the needs for CSR in Agriculture?
23% of companies had “environment and sustainability” as their CSR priority area.
|
Common Areas of CSR and Agriculture |
|