7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
The recent announcement of the Digital India Act, 2023 (DIA) represents a significant step towards establishing a future ready legal framework for the country’s burgeoning digital ecosystem.
|
Status of Internet Usage in India |
|
It replace the two-decade-old Information Technology Act of 2000 which regulated personal data.
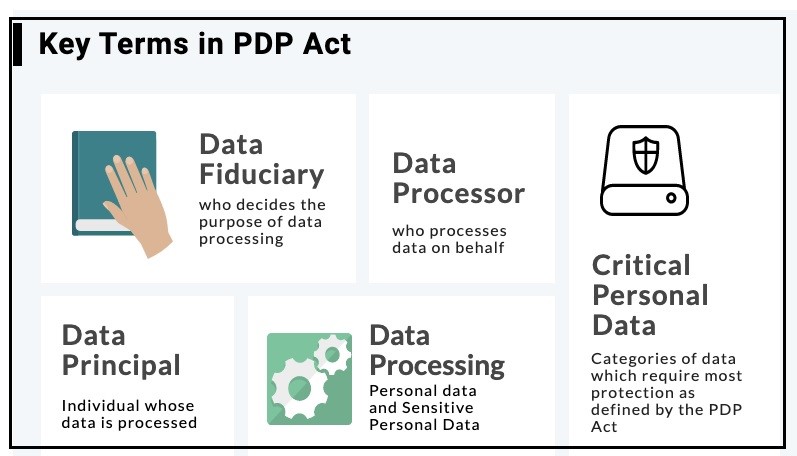
To know more about the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill 2023, click here
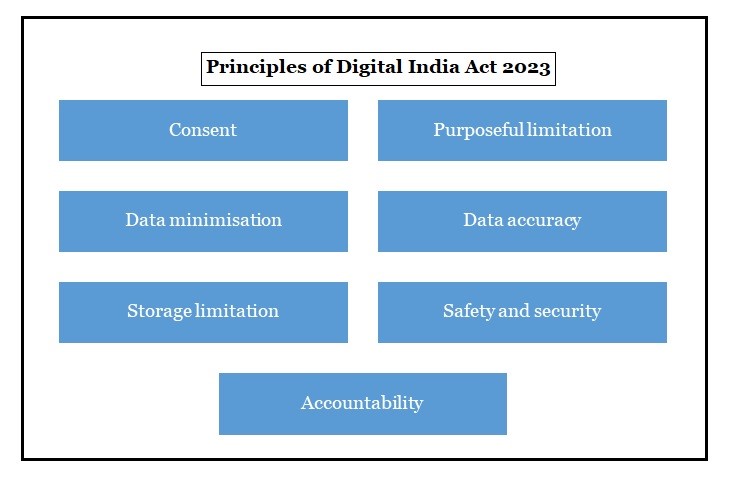
Principles of DIA 2023
References