7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
The role of Farmer Producer Organisation (FPO) as engines of agri innovation has made the Eastern Uttar Pradesh a hub of vegetable and fruit exports.
Sahyadri Farms is India’s largest farmer producer company with over 8,000 farmer shareholders.
Lokhit Bahuuddeshiya Krishi Producer Company is a women-led FPO that cultivates organic cotton and sells it to global brands.
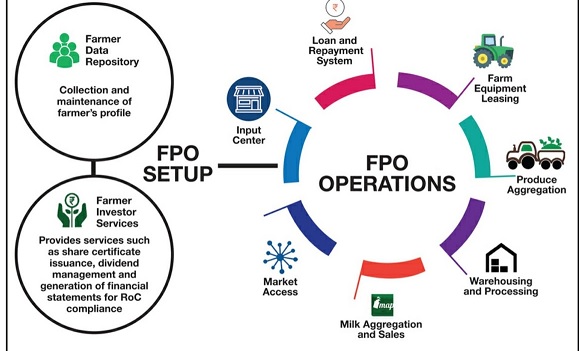
Activities involved
|
Steps taken by the Government to promote FPOs |
|
References