7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
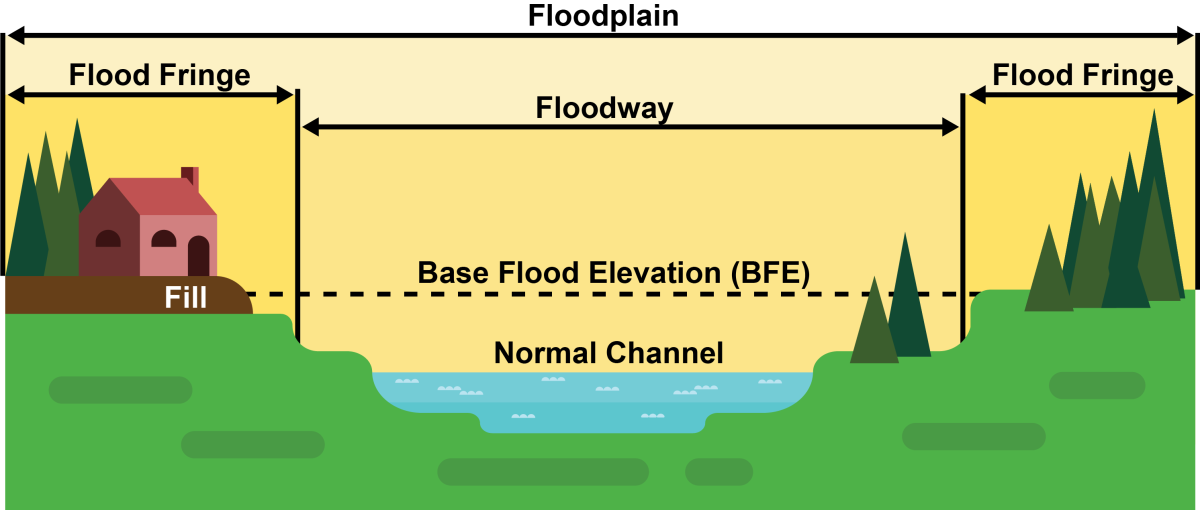
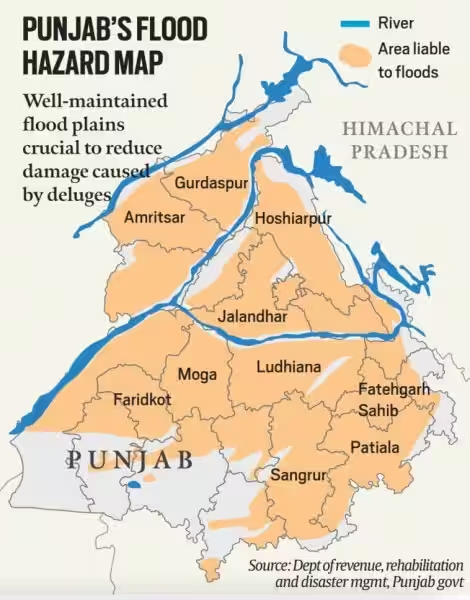
Punjab is witnessing flood for over a month now. The villages along the rivers Sutlej, Beas, Ravi and Ghaggar are the worst affected.
References