7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
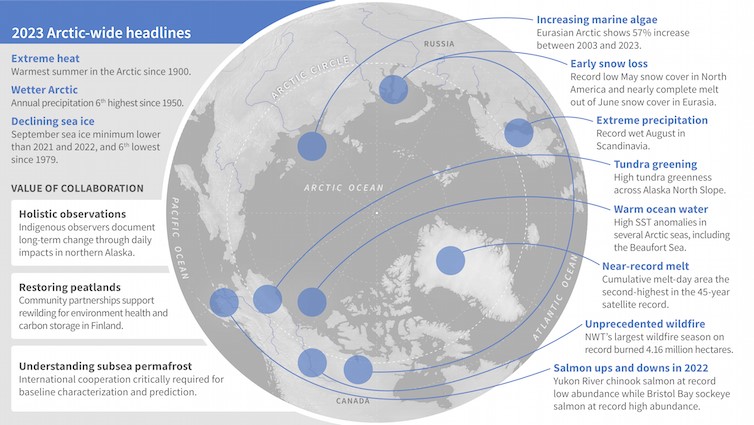
Recently the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) released the annual Arctic report card 2023.
|
About |
Description |
|
Warmest summer |
|
|
Feedback loops |
|
|
Arctic sea ice extent |
|
|
Greenland ice sheet |
|
|
Arctic tundra |
|
|
Arctic ocean |
|
|
Arctic precipitation |
|
|
Arctic wildfires |
|
|
Arctic climate change |
|
To know about Arctic research click here