Currently, multiple favourable weather systems have kept the monsoon either active or vigorous (with respect to rainfall events) over southern peninsular, east, northeast, and central India regions.
|
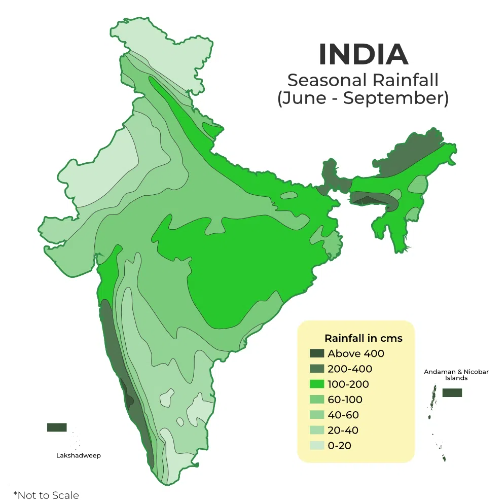
Rainfall Distribution in India |
|
|
Annual Precipitation Levels |
Regions |
|
Extreme (>400cm) |
Northeastern India and windward side of Western Ghats. |
|
Heavy (200-300 cm) |
Eastern Areas and Sub-Himalayan belts |
|
Moderate (100-200 cm) |
Leeward side of Western Ghats and Parts of Central and Eastern India |
|
Scanty (50-100 cm) |
Parts of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Punjab, Haryana, Western UP, TamilNadu, Andhra Pradesh |
|
Very less (<50 cm) |
Majorly in Rajasthan, Gujarat, some parts of Jammu & Kashmir |
How climate change impacts rainfall pattern in India?
|
Impacts of Changing Rainfall Patterns in India |
|
Monsoon trough is a semi-permanent, low-pressure area extending between Pakistan and the Bay of Bengal during the monsoon season which usually oscillates between north and south within the season.