7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Leaders from countries will gather in the Egyptian city of Sharm El-Sheikh for the 27th round of the Conference of Parties (COP27) to deliberate on a global response to the increasing threat of climate change.

What’s on the agenda at the upcoming COP27?
Findings 0f Emissions Gap Report 2022
Findings of the World Resources Institute
Where does India stand?
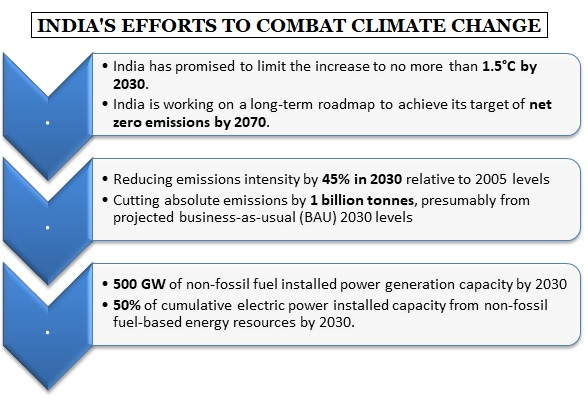
References
Quick facts
Emissions from agriculture industry
- Livestock - Emissions from livestock mainly include carbon dioxide (from urea), nitrous oxide (from livestock dung and urine), and methane (from belching) among others.
- NASA claims that the process of cow belching (burping) releases more methane into the environment due to enteric fermentation.
- Paddy – Paddy cultivation in wetlands prevents oxygen from penetrating the soil and creates suitable conditions for methane-emitting bacteria thus accounting for 8% of human-linked emissions.
- Nitrous oxide and methane absorb more energy than CO2 but stay in the atmosphere for a shorter duration.
- Over a 20-year-period, it has 80 times more GWP than carbon dioxide.
- According to the IPCC, the Global Warming Potential (GWP) of gases is a metric that helps measure the radiative effect (the ability to absorb energy) of each unit of gas over a specific period of time such as 100 years, relative to the radiative effect of carbon dioxide.
- An IPCC research showed methane is responsible for at least a quarter of today’s global warming.
- The UNEP and Climate and Clean Air Coalition 2021 assessment found that cutting human or farming-related methane emissions by 45% this decade is key in the global battle against climate change.