The 2024 Economics Nobel prize was awarded to U.S. economists Daron Acemoglu, Simon Johnson and James A. Robinson “for studies of how institutions are formed and affect prosperity.”
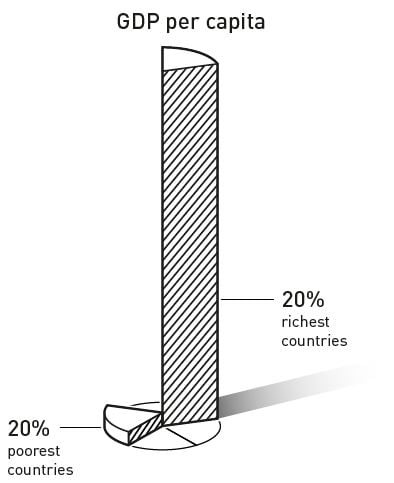
The book “Why Nations Fail: The Origins of Power, Prosperity, and Poverty” written by Daron Acemoglu and James A. Robinson.
|
Characteristics |
Inclusive Institutions |
Extractive Institutions |
|
They are the Economic and Political institutions of a country. |
||
|
Property Rights |
They secure private property rights and democracy. |
They insecure private property rights. |
|
They prevent the State from seizing the property of honest citizens. |
They legalize expropriation of properties from citizens. |
|
|
Citizens |
They incentivize citizens to work hard without the fear of expropriation. |
They affect individual incentives negatively. |
|
They encourage citizens to grow and develop. |
They capitalise on its population with an exploitative intent. |
|
|
Economic Growth |
They lead to general economic prosperity. |
They cause economic stagnation.
|
|
They promote long-run economic growth and higher living standards. |
They cause economic degradation and poverty. |
|
|
Political Freedom |
Enables political freedom. |
Lack of political freedom |
|
Rule of law |
Better |
Poor |
|
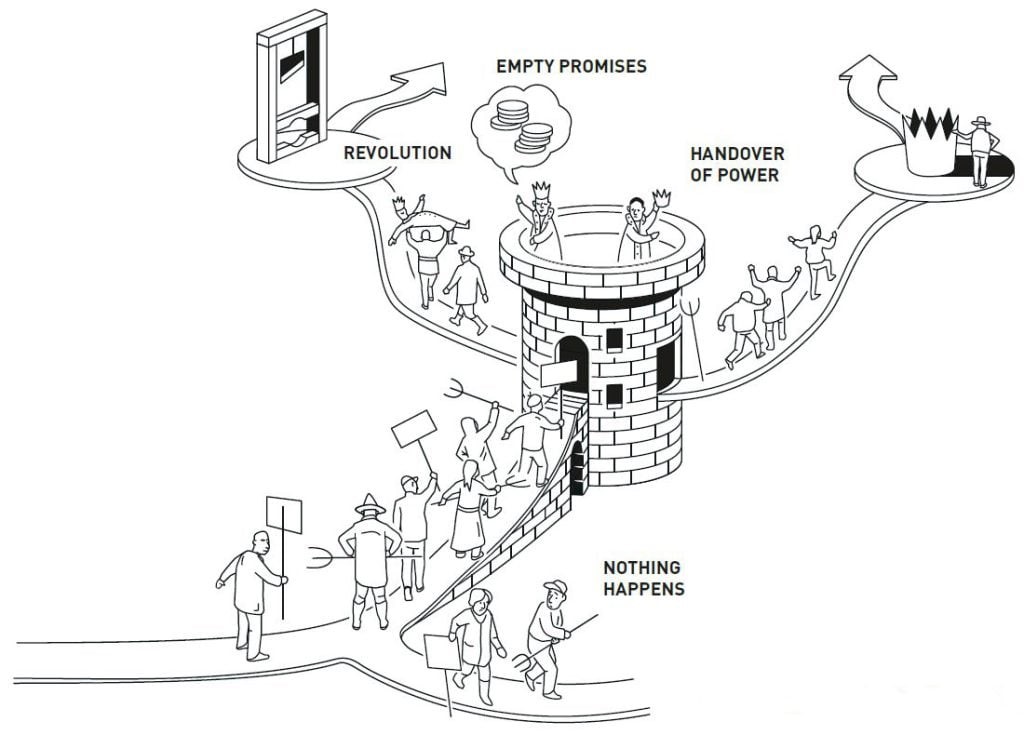
Benefits |
Long-term benefits for everyone. |
Short-term gains for the people in power. |
|
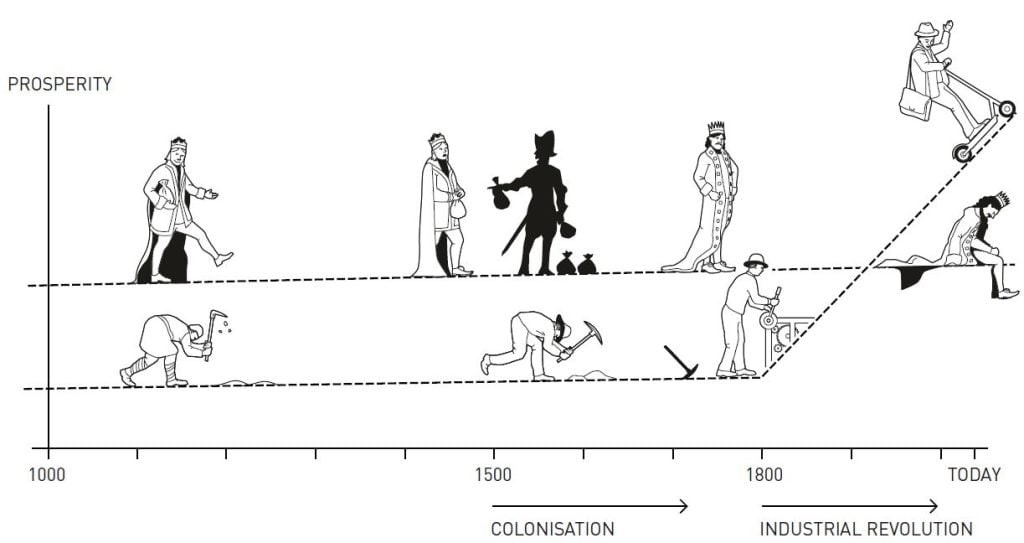
Colonial History |
When Europeans colonised large parts of the globe, the institutions in those societies changed. |
|
|
These are set up by colonists to settle for the long-run. |
These are setup by colonists when they did not want to settle in a certain country. |
|
|
They were introduced in countries that were poor and sparsely populated when they were colonised. |
They were introduced in countries that were rich and densely populated when they were colonised. |
|
|
Example: USA
Here British set up inclusive institutions that promoted long-term economic prosperity and encouraged investment. |
Example : India
Here British set up institutions to plunder the maximum resources within a short span of time. |
|
|
Incidence of disease |
The places where diseases were most dangerous for Europeans now have dysfunctional economic systems and the most poverty, as well as the greatest corruption and weakest rule of law. |
|
References