7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
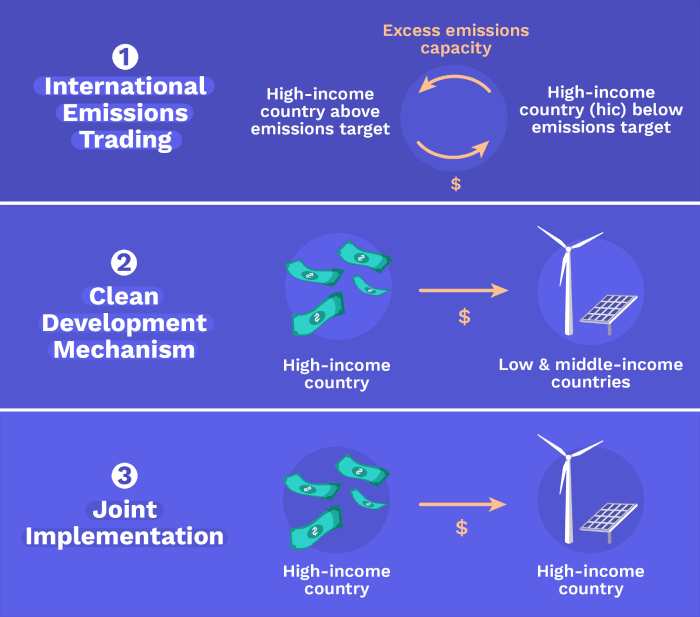
The conclusion of Article 6 of Paris agreement has remained unresolved since the accord was signed and it will be one of the most technical and highly contentious issues at the upcoming UNFCCC COP26.
China, the United States, and European Union are the three largest GHG emitters on an absolute basis. Per capita greenhouse gas emissions are highest in the United States and Russia.
Source: The Hindu