7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Why in news?
Over the years, Lok Sabha’s gender composition has shown a general trend towards increasing women’s representation, but progress has been slow and not linear.
What is the current trend of women's participation in politics?
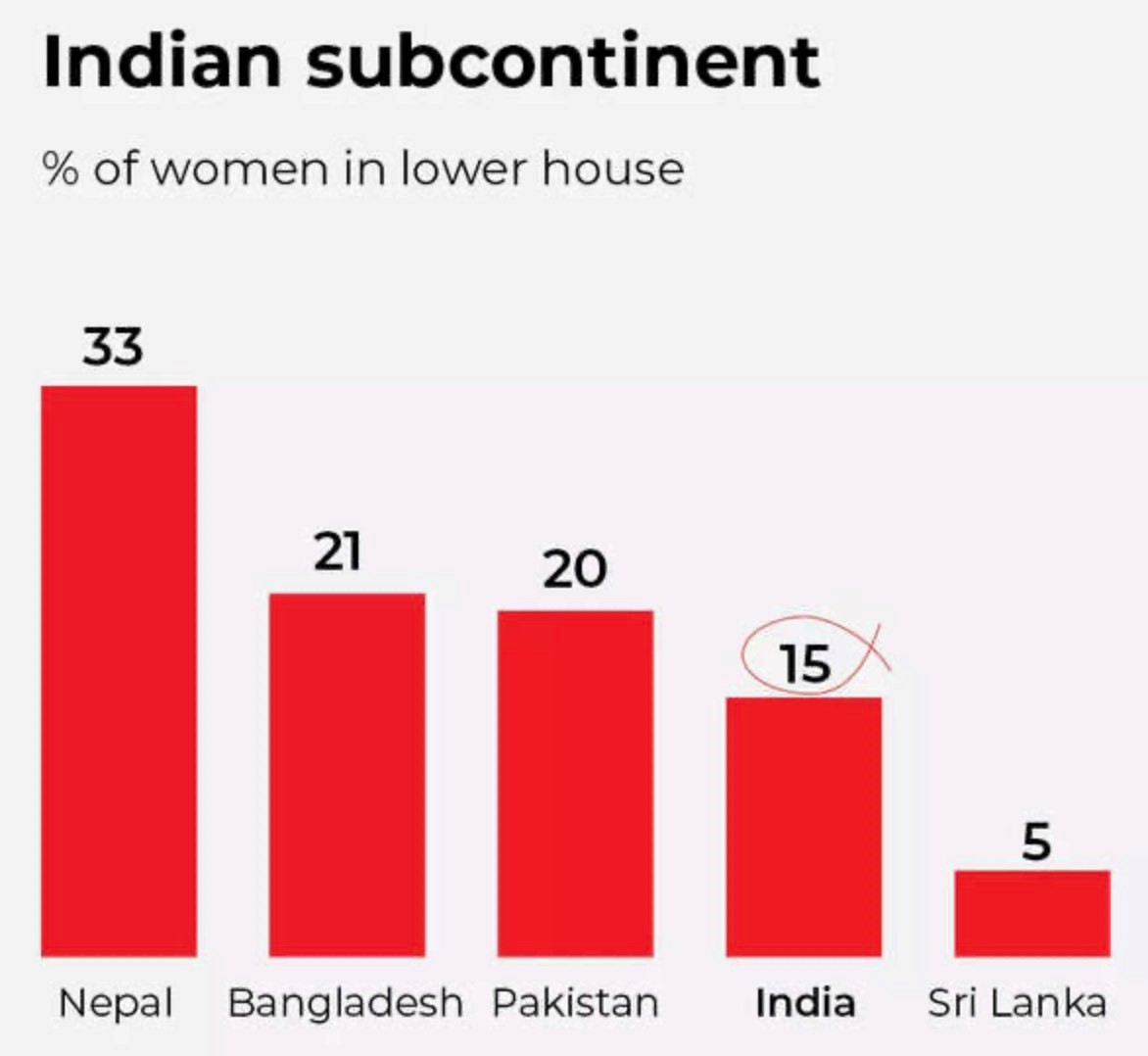
What are the major challenges regarding women's Participation in politics?
|
Global regulatory landscape of women in politics |
|
What should be done?
|
Constitutional rights of women |
|
References