7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
New HIV cases down in India by 44% since 2010.
First cases of HIV AIDS were detected in the 1980s.
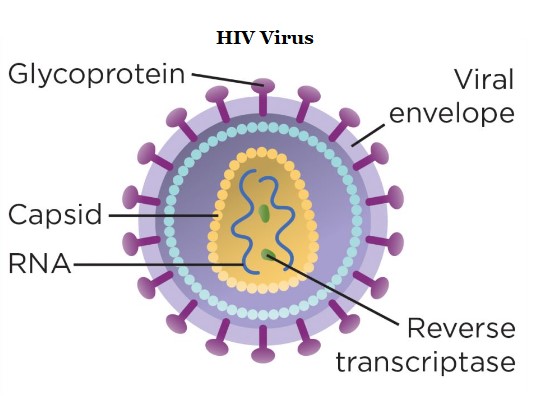
CD4 cells also known as CD4 T lymphocytes or "helper T cells” help fight infection by triggering immune system to destroy viruses, bacteria, and other germs.
The first antiretroviral drug, AZT (zidovudine), was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) in March 1987.