7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
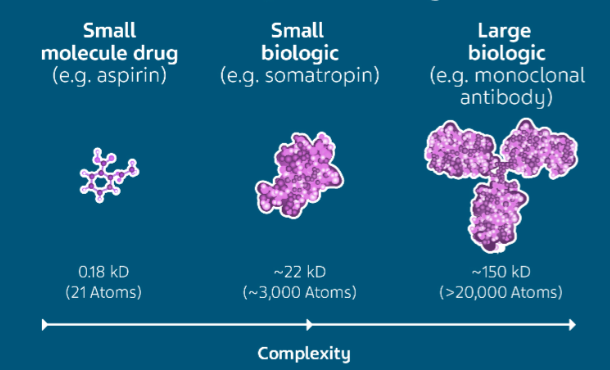
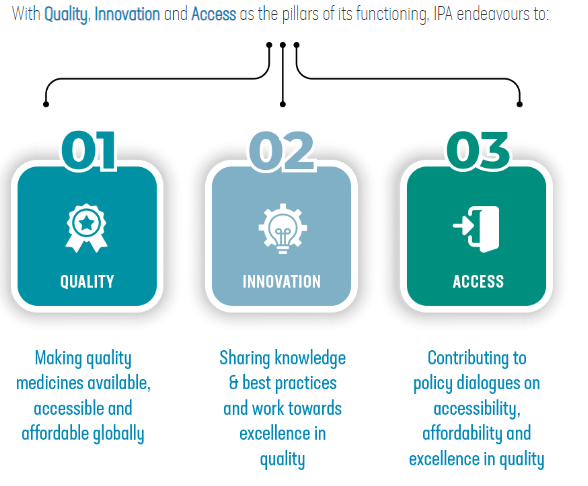
Recently, the biopharmaceutical alliance was launched to build a resilient supply chain in the biopharmaceutical sector.

|
India's Pharmaceutical Sector |
|