7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
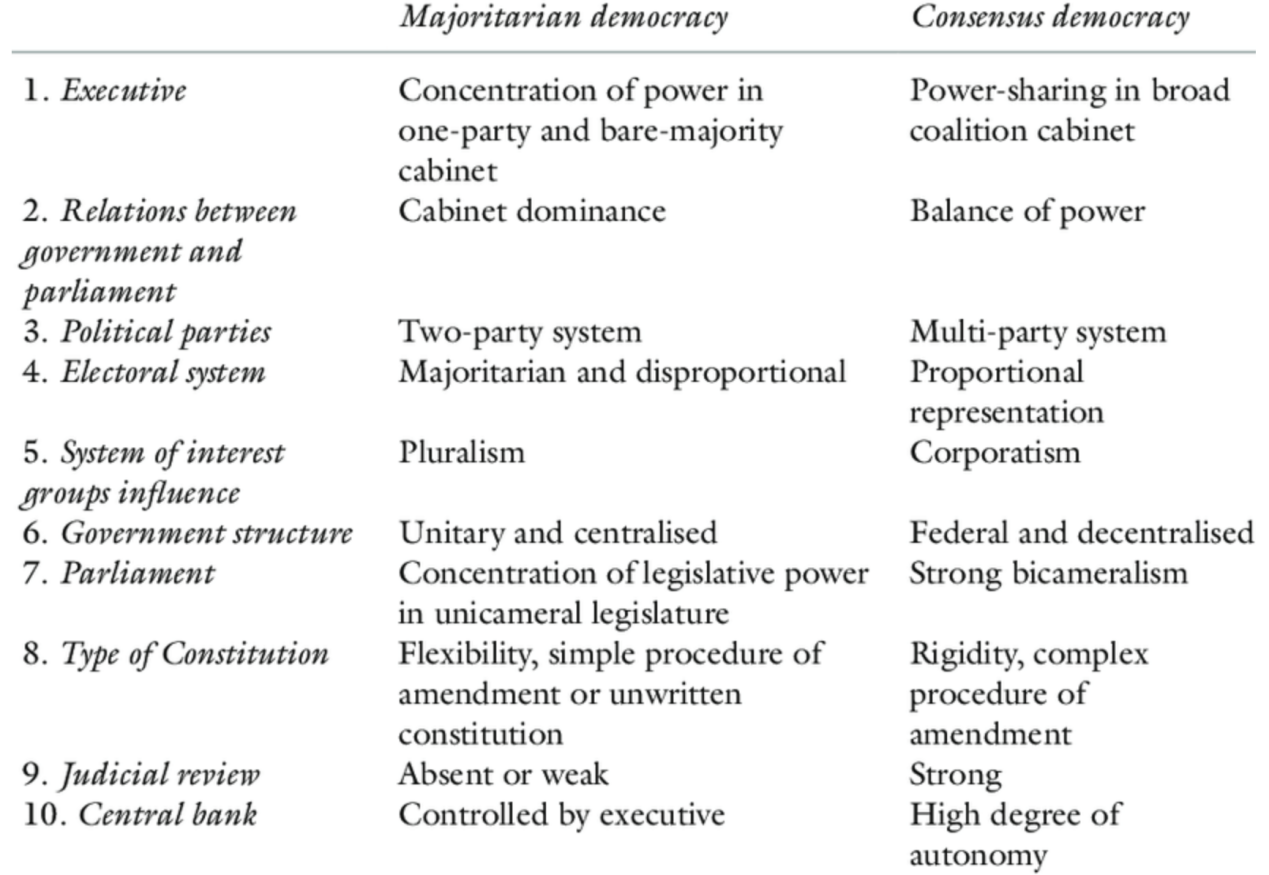
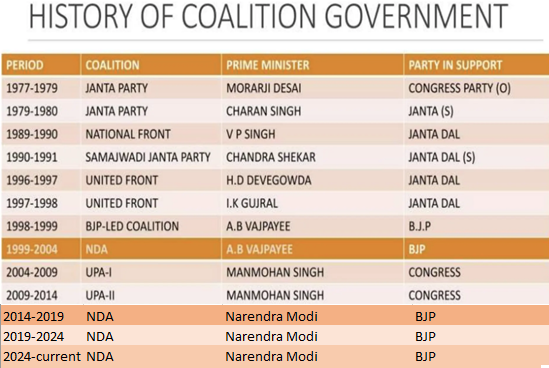
Recently, Coalition politics has made a comeback at the national stage after 10 years of a de facto one-party rule.
|
Coalition Government |
|
|
Merits |
Demerits |
|
|