November 26 of 2024 year will mark the commemoration of the 75th anniversary of the adoption of the Constitution of India.
|
India’s Constitutional Journey |
|
|
1946 |
Cabinet mission is dispatched to India to discuss modalities for transfer of power. |
|
9 Dec 1946 |
Constituent assembly convenes for the first time |
|
29 Aug 1947 |
Establishment of drafting committee |
|
4 Nov 1949 |
Draft is finalized and submitted |
|
26 Nov 1949 |
Constituent Assembly adopts final draft making it official |
|
26 Jan 1950 |
Entry into force of the new constitution |
|
The Constituent Assembly took 2 years, 11 months and 17 days to complete drafting the Constitution for Independent India. During this period, it held 11 sessions covering a total of 165 days. |
|
As India celebrated the 75th year of its constitutional journey in 2024, it is crucial to reflect on the role the Constitution has played in shaping India's democracy, governance, and legal framework. |
|
|
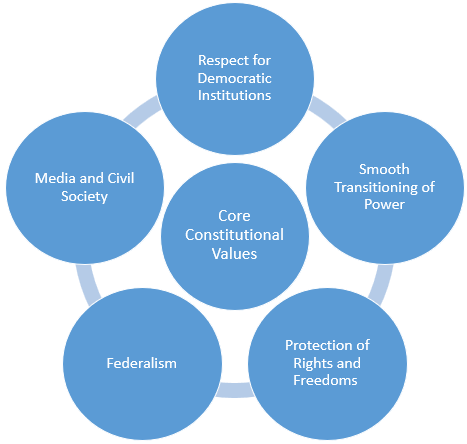
Features of Indian Constitution |
|
Reference
The Hindu| An Approaching Milestone In Constitutional Governance