7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Why in news?
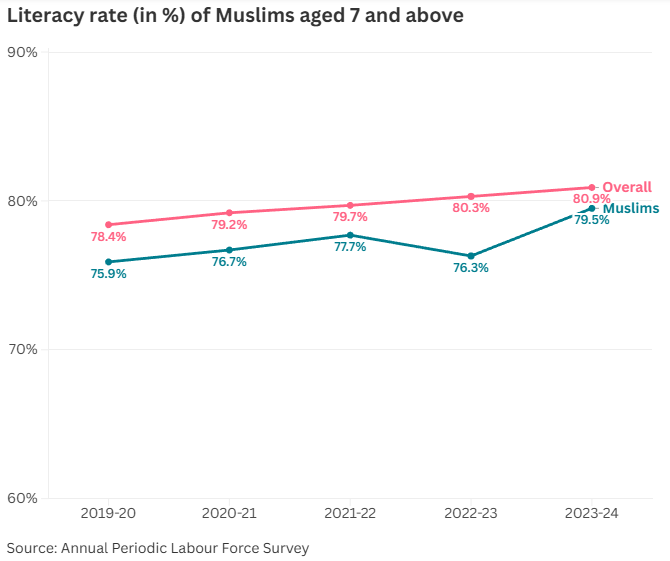
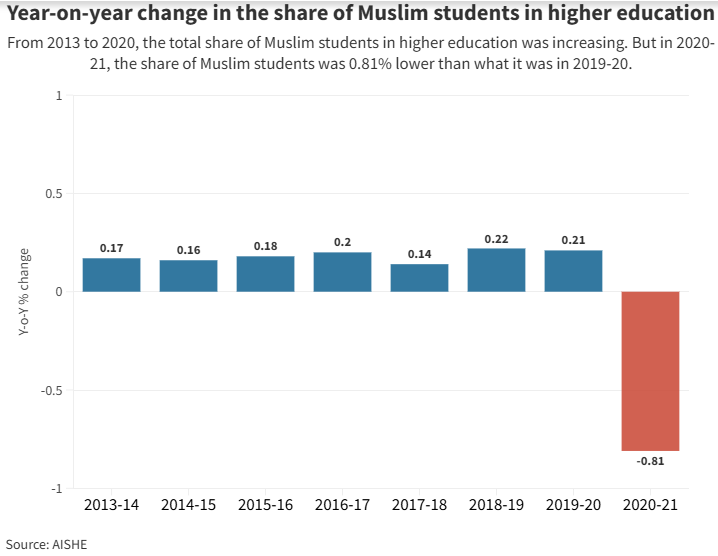
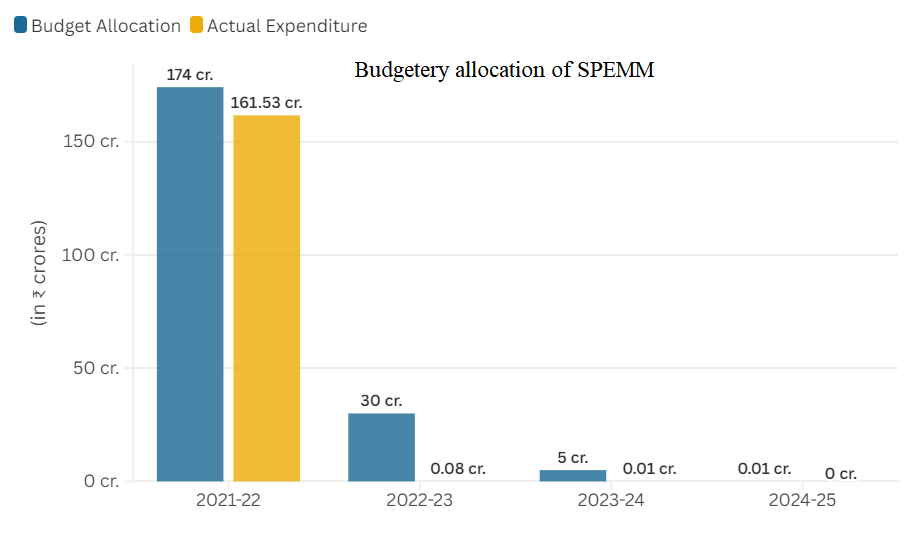
Recently, the Centre had revealed that the budgetary allocations for madrasa and Waqf educational schemes had been lashed almost to nil.
|
|
Central Waqf Council is a statutory body under the Ministry of Minority Affairs was set up in 1964 to advice the Central Government on matters concerning the working of the Waqf Boards.
Madrassas have been centers of Islamic education, dating back to the 8th-9th century during the Abbasid Caliphate.
|
Regions |
Centre |
State |
|
North-Eastern states & Himalayan states |
90% |
10% |
|
Union Territories without legislature |
100% |
- |
|
Other states |
60% |
40% |
The Hindu | Drop in Funding for Waqf Educational Schemes