7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
15th BRICS Summit is set to be held in Johannesburg from 22-24 August 2023.
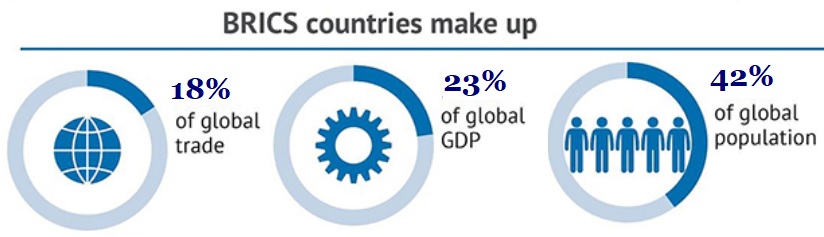
What is the need for BRICS?
In Fortaleza declaration, New Development Bank was created in 2015 worth 100 bn dollars.
References