7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
The presence of leaders from South Asia and the Indian Ocean at the swearing in of Indian PM underlines India’s continuing commitment to the ‘neighbourhood first’ policy.
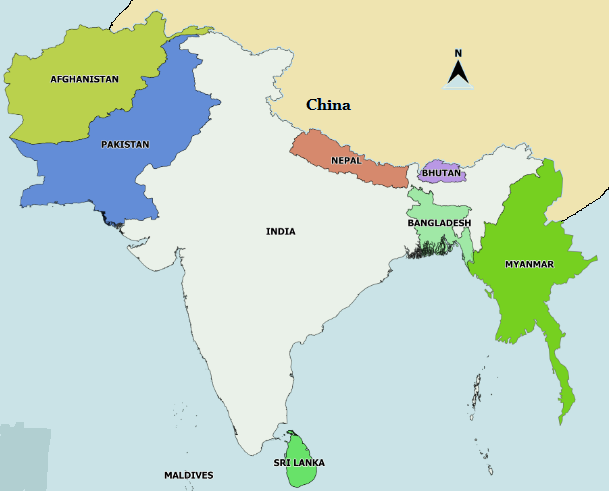
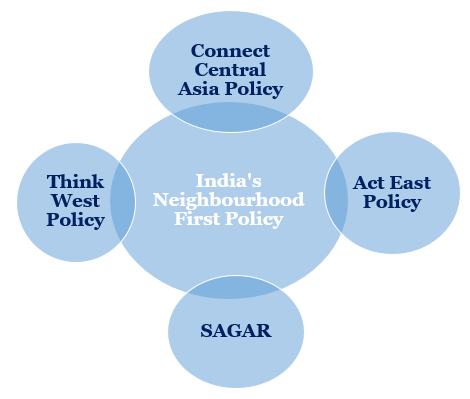
India has enhanced its engagement in the Southeast Asian region through engagements with ASEAN, East Asia Summit, Indian Ocean Rim Association, Indian Ocean Commission, Indian Ocean Naval Symposium, QUAD, among others.
To know about India’s bilateral neighborly relations, click here
|
Gujaral Doctrine |
|
|
Neighbourhood First policy - Succeeded |
|
|
Neighbourhood First policy – Challenges and failures |
|