7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Iran and Afghanistan are locked in a long-standing dispute over the sharing of water from the Helmand River.
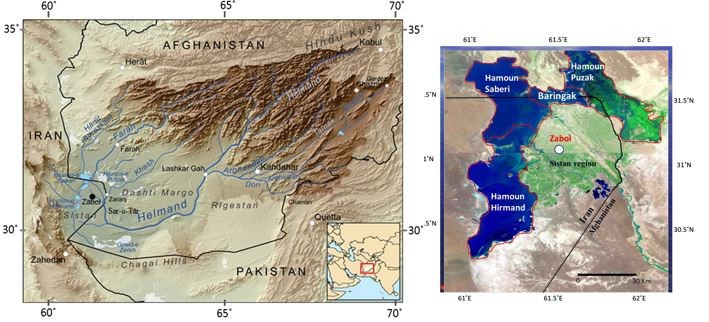
According to Iran’s parliament, 25% to 30% of the population has left the region over the past two decades because of the water shortages.