7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Recently heavy rains severely affected cities across Gujarat, and responses of local bodies have been commented.
The first municipal body was established in Madras in 1687, followed by Bombay and Calcutta.
In 1882, Lord Ripon ,father of local self-government in India, introduced the resolution for local-self-governments, thereby laying the foundations of a democratically elected municipal government to manage cities.
Government of India Acts 1935 recognised the importance of local self-governments and they were treated under provincial or state subjects.
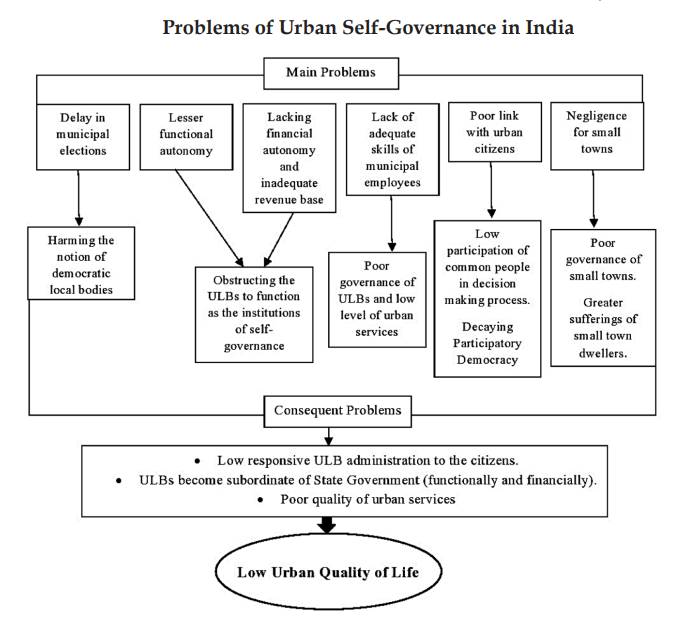
What steps can be taken to empower ULBs?
Reference
The Indian Express | Significance of Empowering Local Bodies