7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
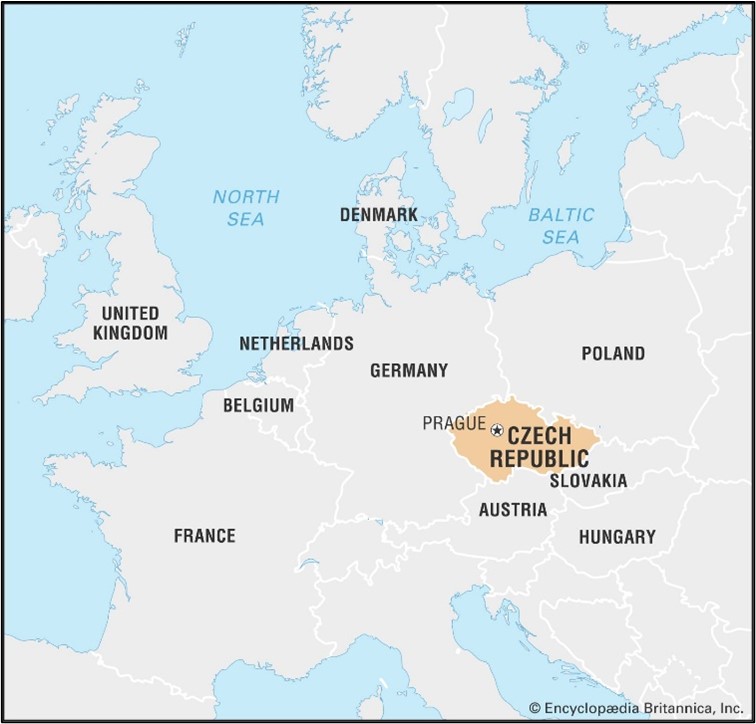
February 24 marks one year since Russia began its invasion of Ukraine.
Socio-economic concerns
Environmental Concerns
References