7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
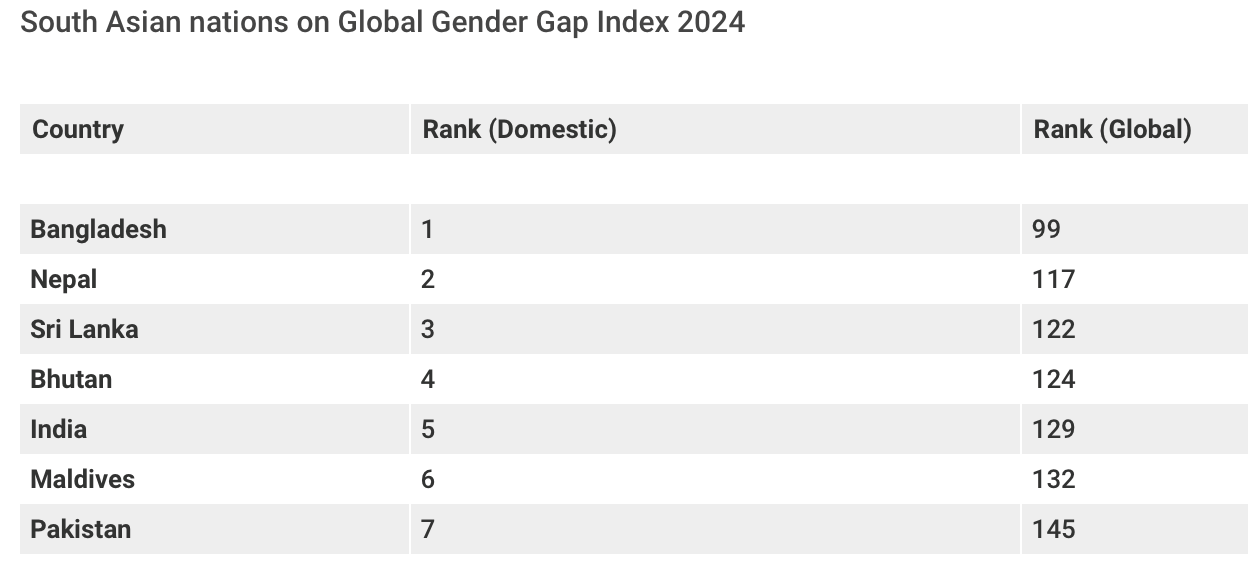
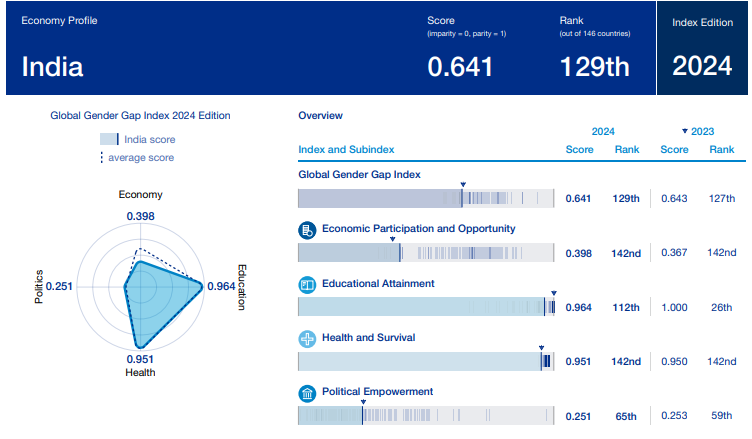
The recent 2024 edition of the Global Gender Gap Index places India at 129 out of the 146 countries it surveyed.
Southern Asia ranks seventh among eight global regions, with a gender parity score of 63.7% and an improvement of 3.9% points since 2006, with Bangladesh, for the first time in the region, having achieved a double-digit rank of 99.