World Health Day, observed annually on 7 April, that highlights global health issues and mobilises action to improve public health outcomes.

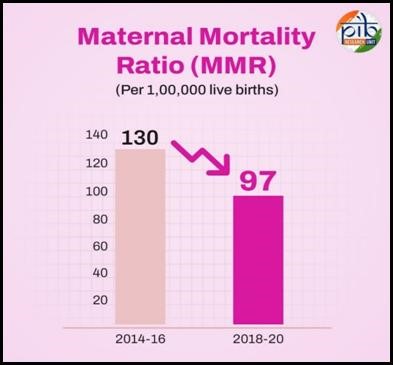
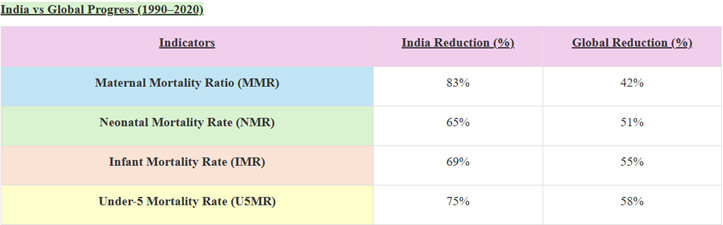
|
Government Programmes for Maternal and Child Health |
|
|
|
Government Programmes for affordable health coverage |
|
What is India’s progress in digital health interventions?
|
Government Programmes for Digital Health |
|
What is India’s progress in disease elimination & control?
|
Government Programmes for Disease Control |
|
What is India’s progress in mental wellness health interventions?
National institute of mental health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS) headquartered at Bengaluru aims to deliver mental health care and shape national policies through research.
India’s health objectives are in line with Sustainable Development Goal 3, which emphasises good health and well-being.