7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains Syllabus: GS II - Issues relating to poverty and hunger.
Recently the World Bank has released its “Spring 2025 Poverty and Equity Brief”.


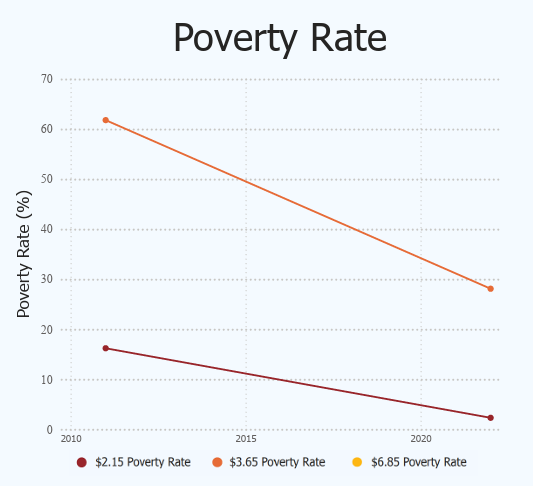


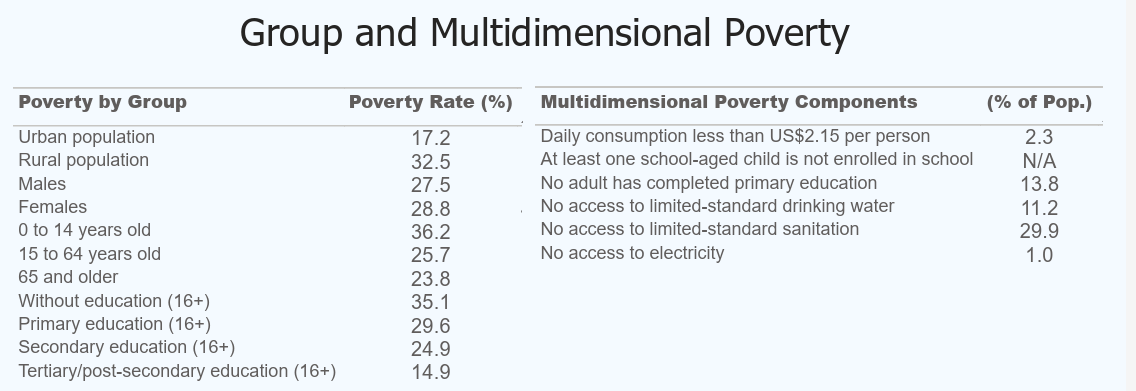

The World Bank’s Multidimensional Poverty Measure (MPM) is adapted from the OPHI MPI. It includes extreme poverty but excludes nutrition and health deprivation.
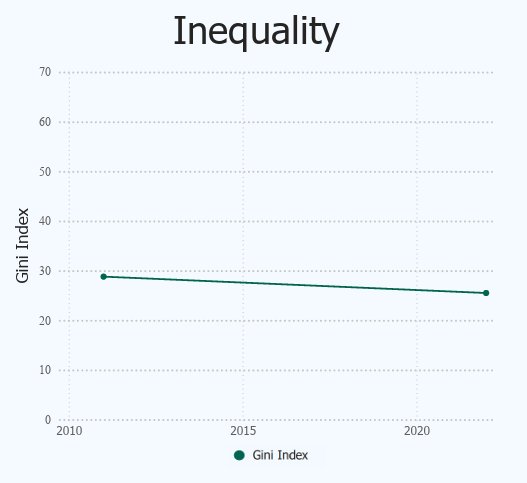
|
Poverty Reduction Measures of India Through targeted welfare schemes, economic reforms, and increased access to essential services, India has made substantial strides in reducing poverty levels. |
|
Affordable Healthcare
|
|
Food Security
|
|
Social Security and Welfare Programs
|
|
Employment And Skill Development
|
|
Entrepreneurship
|