7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
What is the issue?
The Competition Commission of India has slapped a penalty of Rs.873 crore on three beer companies as well as All-India Brewers Association and 11 individuals for colluding to fix beer prices for between 2009 and 2018.
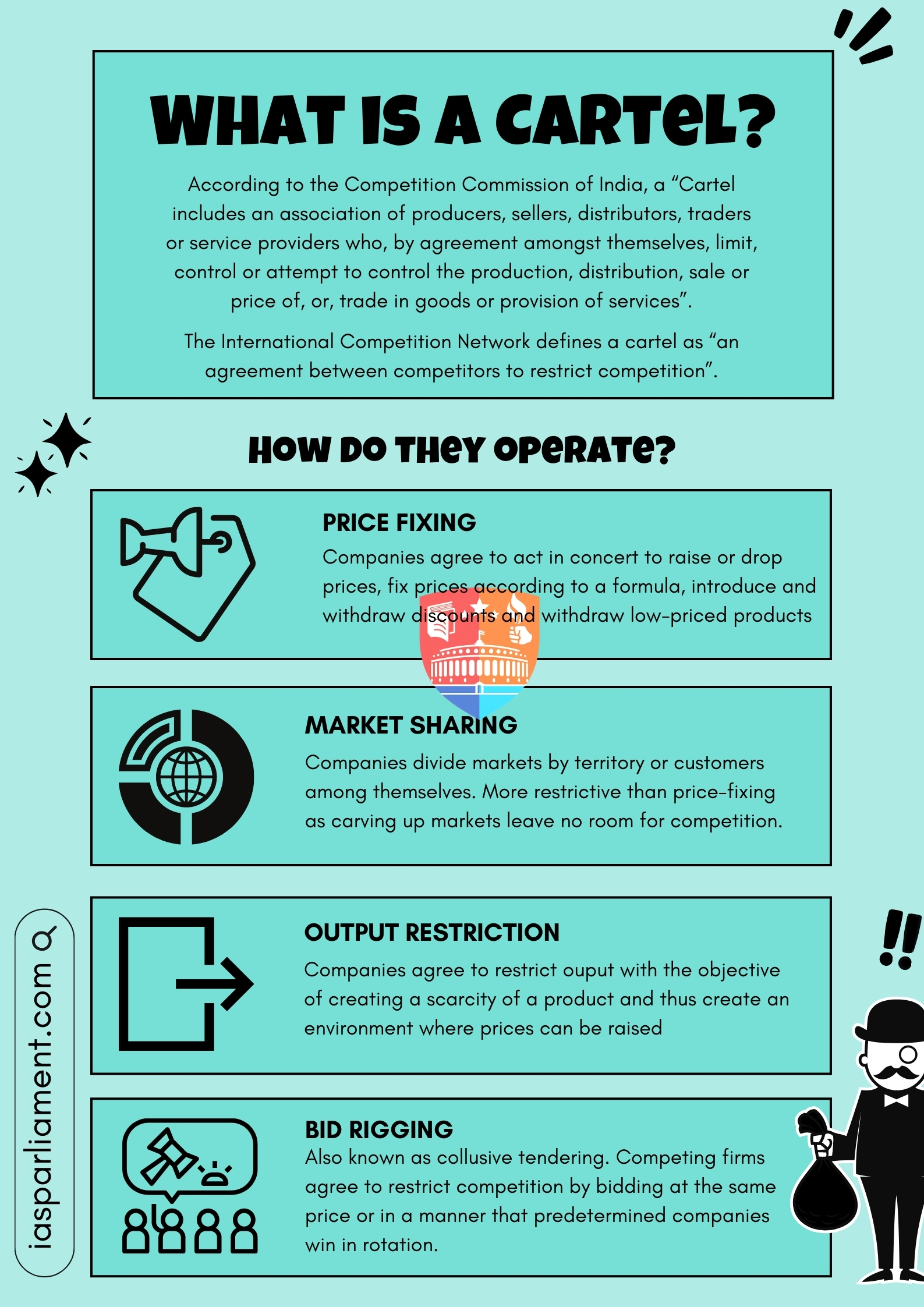
What is a cartel?
How do cartels work?
How do cartels hurt?
How to stop the spread of cartelization?
Source: The Indian Express
Quickfacts
Competition Commission of India (CCI)