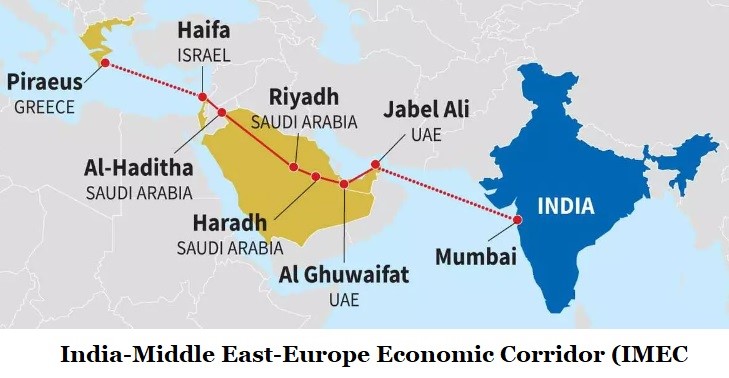
On the sidelines of the G20 Summit, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed to establish the India – Middle East – Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC).
Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII)
|
G7 countries - The United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, and the European Union (EU). |
References
India has proposed to launch the G20 satellite mission for environment and climate observation in the recently held G20 Summit.
References
India announced the launch of the Global Biofuel Alliance on the recently held G20 summit and urged the G-20 nations to join the initiative.
The US, India and Brazil contribute about 85% of the global production and the 81% of consumption of ethanol.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global biofuel production would need to triple by 2030 to put the world’s energy systems on track toward net zero emissions by 2050.
The global ethanol market was valued at $99.06 billion in 2022 and is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 5.1% by 2032 and surpass $162.12 billion by 2032.
References
Small island nations seek protection from ocean pollution, climate change and appeal to the United Nations maritime tribunal recently.
International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea
References