Recently, the Tamil Nadu government has challenged the actions of its Governor, R.N. Ravi, in the Supreme Court.
|
About |
Description |
|
Articles 153 |
There shall be a Governor for each State. |
|
Executive authority |
|
|
7th Constitutional Amendment Act, 1956 |
It facilitated the appointment of the same person as a Governor for two or more States |
|
Office of Governor |
The Governor is appointed by the Centre (Canadian Model) |
|
Appointment (Article 155) |
By President under his seal and warrant |
|
Oath of office |
|
|
Tenure |
5 years, subject to the pleasure of the President |
|
Resignation |
Addressed to President of India |
|
Legal immunity (Article 361) |
Governor cannot be summoned for questioning except on his/her voluntary willingness to testify in the court in support of his/her controversial deeds. |
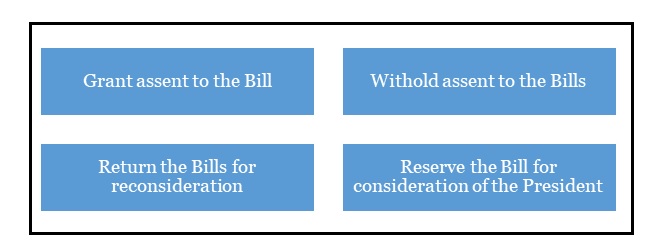
|
Recommendations of Various Commissions |
|
|
Intervention of Judiciary in Governor’s Role |
|
References