7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
What is the issue?
The massive mobilisation of Russian troops on the Ukraine border and occasional outbreak of violence in the contested Donbass region has pushed both countries to the brink of an open conflict.
What is the history of conflict between Ukraine and Russia?
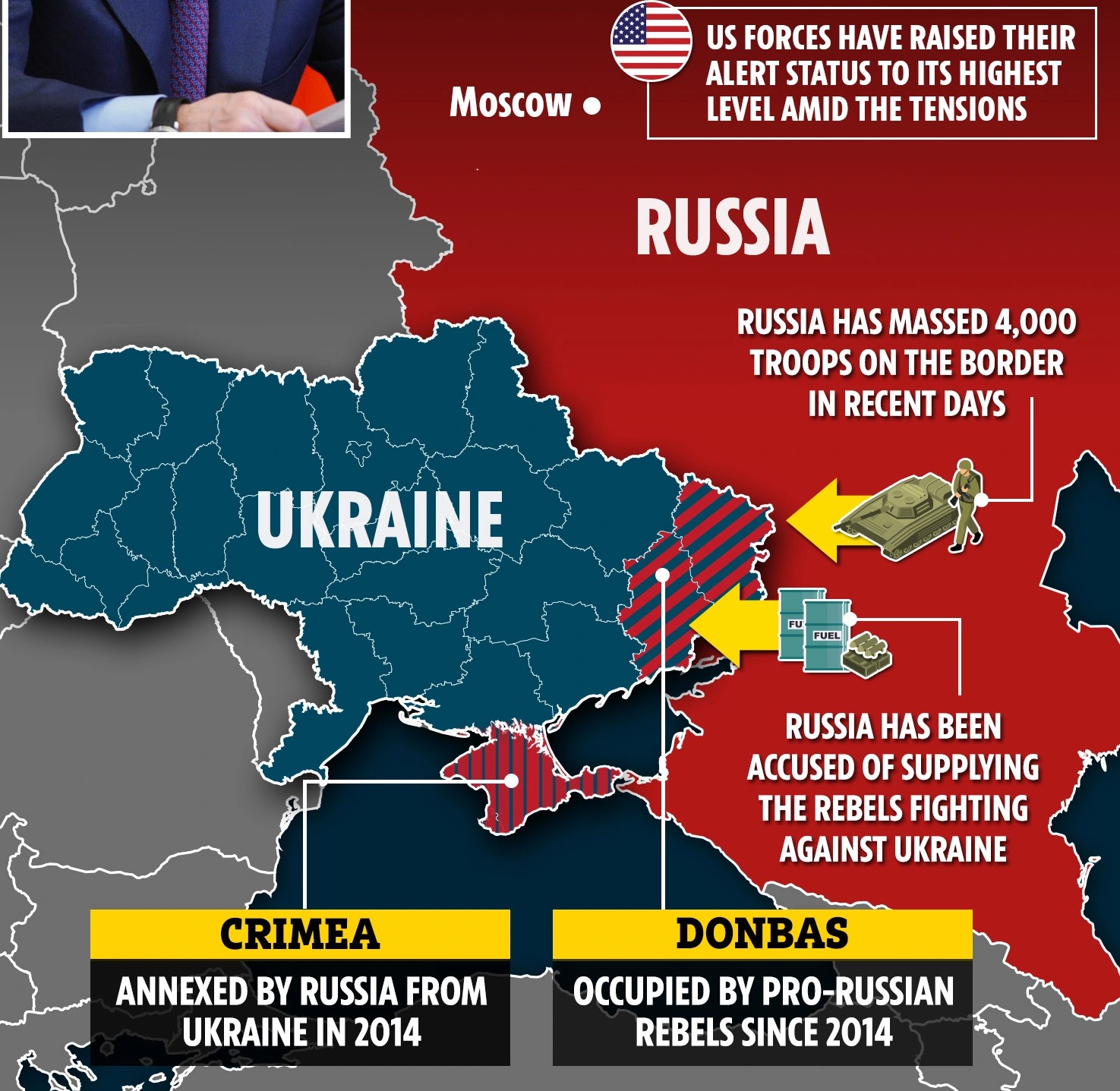
Why is the current conflict more aggressive than the earlier ones?
What are the Minsk Agreements?
What are the practical ways to ease the tension?
References