Recently, the UN General Assembly elected five new members to serve as non-permanent members of the UN Security Council.
United Nations (UN) is a global diplomatic and political organization dedicated to international peace and stability.
Denmark, Greece, Pakistan, Panama and Somalia to serve as non-permanent members on the Security Council for two-year terms from 2024 to 2026 by replacing Ecuador, Japan, Malta, Mozambique and Switzerland.
|
UNSC Member States |
||
|
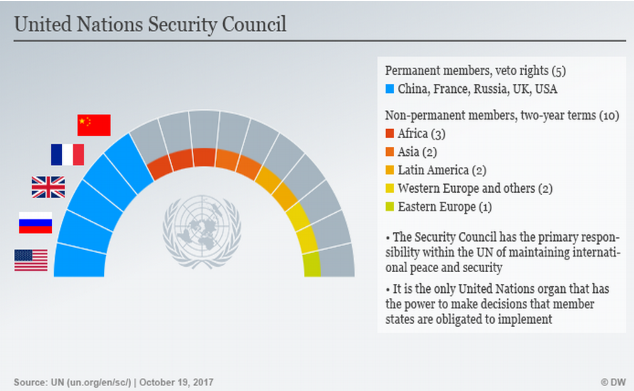
Permanent members |
Non-Permanent Members |
|
|
End Term 2026 |
End Term 2025 |
|
|
USA UK Russia China France
|
Denmark Greece Pakistan Panama Somalia |
Algeria Guyana Republic of Korea Sierra Leona Slovenia |
UNSC also travelled to many cities, holding sessions in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, in 1972, in Panama City, Panama, and in Geneva, Switzerland, in 1990.
UNSC is the only U.N. body that can make legally binding decisions such as imposing sanctions and authorizing use of force.
|
India in UNSC |
|
Under the United Nations Charter, the functions and powers of the UNSC are:
The G4 countries includes Brazil, Germany, India and Japan which was created in 2004.
The L.69 group is a group pro-reform member states, including primarily developing countries from Africa, Latin America and the Caribbean, Asia and the Pacific. It currently has 42 countries as its members including India.
References