Prelims - Current events of national and international importance.
Why in News?
Recently, Union Minister of State for Labour & Employment led the Indian delegation at the BRICS Labour & Employment Ministers’ Meeting held under Brazil’s Presidency in Brasília, Brazil.
|
BRICS |
|
The BRICS Labour & Employment Ministers’ meeting under the Indian Presidency has been convened in 2016 at New Delhi.
Quick Facts
Reference
PIB| 11th BRICS Labour & Employment Minsters Meeting
Related News - Mission LiFE
Prelims - Current events of national and international importance| Economic and Social Development – Sustainable Development, Poverty, Inclusion, Demographics, Social Sector initiatives, etc
Why in News?
In Financial Year 2024-25, India saw a record 4,515 adoptions, the highest in nearly a decade and of these, 4,155 were domestic, marking a powerful shift in societal attitudes.
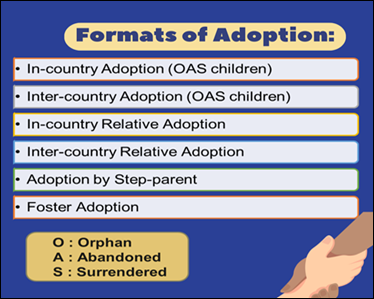
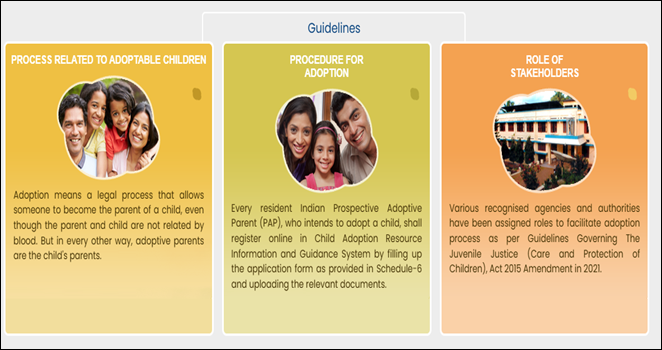
|
Recent Status of Child Adoption in India |
|
References
Prelims (GS I) – Current events of national and international importance| Environmental ecology, Bio-diversity and Climate Change.
Mains (GS I) – Conservation
Why in news?
Recently, the Odisha government officially notified Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR) as a National Park.
Similipal is also a wildlife sanctuary, tiger reserve, UNESCO biosphere reserve and elephant reserve.
The tigers of Similipal possess higher-than-normal levels of melanin, giving them coats that are blacker with yellow stripes and are described as pseudo-melanistic tiger.
The pseudo-melanistic tiger is a colour variant of the Bengal tiger and its strange coat is a result of a mutation in a particular gene.
Greater Similipal Landscape Programme
Reference
The Indian Express| Similipal designated Odisha’s second national park
Prelims – Current events of national and international importance
Why in News?
Recently, Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA) launched Essential Book on the Preservation and Interpretation of India's Manuscript Heritage.
IGNCA was initially conceptualised and launched in 1985 at a function where 5 rocks from 5 major rivers – Sindhu, Ganga, Kaveri, Mahanadi and the Narmada (where the most ancient ammonite fossils are found) were composed into sculptural forms.
|
6 Functional Units of IGNCA |
|
References
Prelims (GS I) – Current events of national and international importance| General issues on Environmental ecology, Bio-diversity and Climate Change.
Mains (GS I) – Conservation
Why in news?
A recent study published in Nature Climate Change provides a global perspective on how UHI impacts both heat and cold related mortality.

Implications of UHI
Way forward
Reference
|
One Liners 29-03-2025 |
|
|
History, Art and Culture |
|
|
Bajirao Ballal Baji Rao I, also known as Bajirao Ballal, was a significant figure in the Maratha Empire passed away on 28th April 1740 at Raverkhedi, near the banks of the Narmada River in present-day Madhya Pradesh.
|
|
|
Geography |
|
|
Netravathi river Recently, Kallapu-Sajipa Riverfront Road project along Netravathi river in Mangaluru receives a Rs 40 crore boost from the state government.
About Netravathi River - A significant west-flowing river in Karnataka, India, also known as the Nethravathi Nadi.
|
|
|
International Relations and Issues |
|
|
World Day for Safety and Health at Work The World Day for Safety and Health at Work is observed annually on April 28th.
|
|
|
Economy |
|
|
National Industrial Corridor Development Corporation (NICDC) Recently, NICDC was honoured with the Udyog Vikas Award during the Udyog Vikas event organised by Janmabhumi Daily, a leading news daily in the state of Kerala.
|
|
|
Environment |
|
|
Tree Shrews of South Asia Recent research by the Zoological Survey of India has transformed the understanding of South Asian tree shrews.
|
|
|
Security |
|
|
Indian Ocean Ship (IOS) SAGAR Recently, IOS SAGAR reached Port Louis Harbour, Mauritius after finishing Phase I of joint Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) surveillance with the National Coast Guard (NCG) Mauritius. This surveillance was part of its deployment to the South Western Indian Ocean.
|
|
|
Science |
|
|
Dr. K. Kasturirangan: A Legacy of Space and Education Recently, former ISRO Chairman Dr. Kasturirangan's passing on April 25, 2025, at 84, marks the loss of a visionary who profoundly impacted India's space program and education system, inspiring generations.
|
|
|
Miscellaneous |
|
|
National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology (NIELIT) Recently, NIELIT signs MoUs with 8 Visionary Organizations to Propel Digital India Initiatives.
|
|
|
World Veterinary Day 2025 Recently, World Veterinary Day 2025, was observed on April 26th.
|
|
|
Prestigious French Award Recently, Mumbai filmmaker Payal Kapadia received the ‘Officier dans l’Ordre des Arts et des Lettres’ from the French Government for her cinematic contributions.
|